MicroRNA 744-3p promotes MMP-9-mediated metastasis by simultaneously suppressing PDCD4 and PTEN in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27533461
- PMCID: PMC5295426
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11280
MicroRNA 744-3p promotes MMP-9-mediated metastasis by simultaneously suppressing PDCD4 and PTEN in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
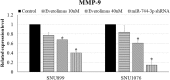
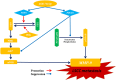
MicroRNA controls cancer invasion by governing the expression of gene regulating migration and invasion. Here, we reported a novel regulatory pathway controlled by miR-744-3p, which enhanced expression of matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9) in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). We profiled the differential micoRNA expression pattern in LSCC cell lines and normal epithelial cultures derived from the head and neck mucosa using microRNA microarray. MiR-7-1-3p, miR-196a/b and miR-744-3p were expressed differentially in the LSCC cell lines. Subsequent validation using real-time PCR revealed that high miR-744-3p level was positively correlated with regional lymph node metastasis of LSCC. Real-time cellular kinetic analysis showed that suppressing miR-744-3p could inhibit migration and invasion of LSCC cell lines and reduce the number of lung metastatic nodules in nude mice modules. In silico analysis revealed that miR-744-3p targeted 2 distinct signaling cascades which eventually upregulated MMP-9 expression in LSCC. First, miR-744-3p could suppress programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), a direct suppressor of NF-κB (p65). PDCD4 could also prevent AKT activation and suppress MMP-9 expression. Further, suppressing miR-744-3p expression could restore phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) expression. PTEN could inhibit AKT activation and inhibit MMP-9 expression in LSCC cells. The results revealed that suppressing miR-744-3p was effective to inhibit LSCC metastasis by inactivating AKT/mTOR and NF-κB (p65) signaling cascade. Targeting miR-744-3p could be a valuable therapeutic intervention to suppress the aggressiveness of LSCC.
Keywords: PDCD4; PTEN; laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma; metastasis; miR-744-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest were declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA‑503 serves an oncogenic role in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting programmed cell death protein 4.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):5249-5256. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7278. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28849168 Free PMC article.
-
miR-144-3p, a tumor suppressive microRNA targeting ETS-1 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 8;7(10):11637-50. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7025. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26826553 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-365a-3p promotes tumor growth and metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2016 Apr;35(4):2017-26. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4617. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26883008
-
Prospects for miR-21 as a Target in the Treatment of Lung Diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(3):415-422. doi: 10.2174/1381612826999200820160608. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 32867648 Review.
-
Small in Size, but Large in Action: microRNAs as Potential Modulators of PTEN in Breast and Lung Cancers.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 18;11(2):304. doi: 10.3390/biom11020304. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33670518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA-744 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits the aggressive behaviors by directly targeting NOB1.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Nov 1;8(11):2238-2253. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30555741 Free PMC article.
-
Overview on Molecular Biomarkers for Laryngeal Cancer: Looking for New Answers to an Old Problem.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 28;14(7):1716. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071716. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A natural antisense lncRNA controls breast cancer progression by promoting tumor suppressor gene mRNA stability.PLoS Genet. 2018 Nov 29;14(11):e1007802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007802. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30496290 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑503 serves an oncogenic role in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting programmed cell death protein 4.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):5249-5256. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7278. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28849168 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA in combination with HER2-targeting drugs reduces breast cancer cell viability in vitro.Sci Rep. 2021 May 25;11(1):10893. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90385-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34035375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cattaruzza MS, Maisonneuve P, Boyle P. Epidemiology of laryngeal cancer. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol. 1996;32b:293–305. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. International journal of cancer. 2001;94:153–6. - PubMed
-
- Mirisola V, Mora R, Esposito AI, Guastini L, Tabacchiera F, Paleari L, Amaro A, Angelini G, Dellepiane M, Pfeffer U, Salami A. A prognostic multigene classifier for squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx. Cancer letters. 2011;307:37–46. - PubMed
-
- Ferlito A, Haigentz M, Jr, Bradley PJ, Suarez C, Strojan P, Wolf GT, Olsen KD, Mendenhall WM, Mondin V, Rodrigo JP, Boedeker CC, Hamoir M, Hartl DM, et al. Causes of death of patients with laryngeal cancer. European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology. 2014;271:425–34. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2478-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

