Resolution of Otitis Media With Effusion in Children With Cleft Palate Followed Through Five Years of Age
- PMID: 27533493
- PMCID: PMC5074527
- DOI: 10.1597/15-130
Resolution of Otitis Media With Effusion in Children With Cleft Palate Followed Through Five Years of Age
Abstract
Objective: To describe the temporal pattern of otitis media with effusion (OME) resolution for a cohort of nonsyndromic cleft palate children enrolled before palatoplasty and followed through 5 years of age.
Design: This is a prospective, longitudinal study of the time course for OME resolution in infants and children with palatal clefts.
Setting: Cleft Palate Craniofacial Center of a tertiary care pediatric hospital.
Participants: This study included 52 children with cleft palate (29 boys, 45 white, Veau 1 through 4) who had a Furlow-type palatoplasty between 10 and 24 months of age performed by one of six surgeons.
Interventions: Standard cleft palate management was supplemented with study visits to the research clinic pre- and postpalatoplasty and then yearly to 6 years of age for assessments of middle ear status by interval history, otoscopy, and tympanometry.
Main outcome measure: The main outcome measure was age at otitis media resolution defined as the age in years at the first in a sequence of "disease-free" diagnoses not interrupted or followed by any other diagnosis.
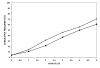
Results: The cumulative percent OME resolution for ears/children at ages <1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 years was 4.1/4.4, 14.3/10.9, 31.6/21.7, 45.9/37.0, 56.1/50.0, and 70.4/60.9%. OME resolution followed a simple linear time curve with slopes of 13.5% (confidence interval [CI] = 12.2% to 14.8%, r(2) = .99) and 11.9% (CI = 10.1% to 13.6%, r(2) = .99) resolutions per year for ears and children, respectively.
Conclusions: There is a natural, age-related pattern of resolution for persistent OME that affects most infants and young children with cleft palate that is not affected by palatoplasty.
Keywords: cleft palate; disease resolution; otitis media with effusion; prospective study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is otitis media with effusion almost always accompanying cleft palate in children?: the experience of 319 Asian patients.Laryngoscope. 2012 Jan;122(1):220-4. doi: 10.1002/lary.22425. Laryngoscope. 2012. PMID: 22183637
-
[Characteristics of secretory otitis media in children with cleft palate and timing of intervention of tympanic membrane].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jul;33(7):647-650. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.07.017. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31327205 Chinese.
-
Prognosis of otitis media with effusion in pediatric patients with cleft palate during language-acquisition period treated by simultaneous tympanostomy tube placement with palatoplasty.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Apr;155:111071. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2022.111071. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35217270
-
Otitis media with effusion in children with cleft lip and palate: a narrative review.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Sep;77(9):1403-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.07.015. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23931986 Review.
-
Cleft palate and otitis media with effusion: a review.Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2003;124(3):171-7. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2003. PMID: 14725133 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between cleft palate width and otitis media.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022 Oct 25;7(6):2126-2132. doi: 10.1002/lio2.933. eCollection 2022 Dec. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 36544954 Free PMC article.
-
Tubomanometry in measurement of velopharyngeal closure: A pilot study.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2023 Mar 9;8(2):554-560. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1039. eCollection 2023 Apr. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37090858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Improved national prevalence estimates for 18 selected major birth defects--United States, 1999–2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2006 Jan 6;54:1301–1305. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli PJ, Jorge JC, Feniman MR, Piazentin-Penna SH, Dutka-Souza JC, Seagle MB, Williams WN, Nackashi JA, Boggs S, Graciano MI, Souza TV, Neto JS, Garla LA, Silva ML, Marques IL, Borgo HC, Martinelli AP, Shuster JJ, Pimentel MC, Zimmermann MC, Bento-Gonçalves CG, Kemker FJ, McGorray SP, Pegoraro-Krook MI. Otologic and audiologic outcomes with the Furlow and von Langenbeck with intravelar veloplasty palatoplasties in unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2011;48:412–418. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bess FH, Schwartz DM, Redfield NP. Audiometric, impedance, and otoscopic findings in children with cleft palates. Arch Otolaryngol. 1976;102:465–469. - PubMed
-
- Bluestone CD, Klein JO. Otitis Media in Infants and Children. 5. Ontario: B. C. Decker, Inc; 2007.
-
- Bluestone CD. Eustachian Tube Structure, Function, Role in Otitis Media. Hamilton, Ontario: BC Decker Inc; 2005.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical