Role of a Lateral Orbital Frontal Cortex-Basolateral Amygdala Circuit in Cue-Induced Cocaine-Seeking Behavior
- PMID: 27534268
- PMCID: PMC5240178
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2016.157
Role of a Lateral Orbital Frontal Cortex-Basolateral Amygdala Circuit in Cue-Induced Cocaine-Seeking Behavior
Abstract
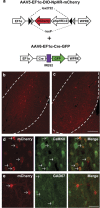
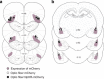
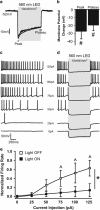
Cocaine addiction is a disease characterized by chronic relapse despite long periods of abstinence. The lateral orbitofrontal cortex (lOFC) and basolateral amygdala (BLA) promote cocaine-seeking behavior in response to drug-associated conditioned stimuli (CS) and share dense reciprocal connections. Hence, we hypothesized that monosynaptic projections between these brain regions mediate CS-induced cocaine-seeking behavior. Male Sprague-Dawley rats received bilateral infusions of a Cre-dependent adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector expressing enhanced halorhodopsin 3.0 fused with a reporter protein (NpHR-mCherry) or a control AAV (mCherry) plus optic fiber implants into the lOFC (Experiment 1) or BLA (Experiment 2). The same rats also received bilateral infusions of a retrogradely transported AAV vector expressing Cre recombinase (Retro-Cre-GFP) into the BLA (Experiment 1) or lOFC (Experiment 2). Thus, NpHR-mCherry or mCherry expression was targeted to lOFC neurons that project to the BLA or to BLA neurons that project to the lOFC in different groups. Rats were trained to lever press for cocaine infusions paired with 5-s CS presentations. Responding was then extinguished. At test, response-contingent CS presentation was discretely coupled with optogenetic inhibition (5-s laser activation) or no optogenetic inhibition while lever responding was assessed without cocaine/food reinforcement. Optogenetic inhibition of lOFC to BLA, but not BLA to lOFC, projections in the NpHR-mCherry groups disrupted CS-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior relative to (i) no optogenetic inhibition or (ii) manipulations in mCherry control or (iii) NpHR-mCherry food control groups. These findings suggest that the lOFC sends requisite input to the BLA, via monosynaptic connections, to promote CS-induced cocaine-seeking behavior.
Figures


References
-
- Brebner K, Childress AR, Roberts DCS (2002). A potential role for GABA(B) agonists in the treatment of psychostimulant addiction. Alcohol Alcohol 37: 478–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

