Precise and selective sensing of DNA-DNA hybridization by graphene/Si-nanowires diode-type biosensors
- PMID: 27534818
- PMCID: PMC4989226
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31984
Precise and selective sensing of DNA-DNA hybridization by graphene/Si-nanowires diode-type biosensors
Abstract
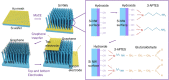
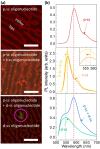
Single-Si-nanowire (NW)-based DNA sensors have been recently developed, but their sensitivity is very limited because of high noise signals, originating from small source-drain current of the single Si NW. Here, we demonstrate that chemical-vapor-deposition-grown large-scale graphene/surface-modified vertical-Si-NW-arrays junctions can be utilized as diode-type biosensors for highly-sensitive and -selective detection of specific oligonucleotides. For this, a twenty-seven-base-long synthetic oligonucleotide, which is a fragment of human DENND2D promoter sequence, is first decorated as a probe on the surface of vertical Si-NW arrays, and then the complementary oligonucleotide is hybridized to the probe. This hybridization gives rise to a doping effect on the surface of Si NWs, resulting in the increase of the current in the biosensor. The current of the biosensor increases from 19 to 120% as the concentration of the target DNA varies from 0.1 to 500 nM. In contrast, such biosensing does not come into play by the use of the oligonucleotide with incompatible or mismatched sequences. Similar results are observed from photoluminescence microscopic images and spectra. The biosensors show very-uniform current changes with standard deviations ranging ~1 to ~10% by ten-times endurance tests. These results are very promising for their applications in accurate, selective, and stable biosensing.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Silicon nanonets for biological sensing applications with enhanced optical detection ability.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Jun 15;68:336-342. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.012. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25599846
-
Fabrication of Ultrasensitive Field-Effect Transistor DNA Biosensors by a Directional Transfer Technique Based on CVD-Grown Graphene.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Aug 12;7(31):16953-9. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b03941. Epub 2015 Jul 30. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26203889
-
Silicon nanowire arrays for label-free detection of DNA.Anal Chem. 2007 May 1;79(9):3291-7. doi: 10.1021/ac061808q. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Anal Chem. 2007. PMID: 17407259
-
Silicon nanowire field-effect-transistor based biosensors: from sensitive to ultra-sensitive.Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Oct 15;60:101-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.03.057. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014. PMID: 24787124 Review.
-
Chemical sensing with nanowires.Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2012;5:461-85. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-062011-143007. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2012. PMID: 22524224 Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications: A Recent Study.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 11;9:1401. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01401. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30914959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanosilicon-Based Composites for (Bio)sensing Applications: Current Status, Advantages, and Perspectives.Materials (Basel). 2019 Sep 6;12(18):2880. doi: 10.3390/ma12182880. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31489913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Synthesis of Carbon Nanoparticles (CNPs) from Biomass for Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 5;24(2):1023. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021023. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tasciotti E. et al. Mesoporous silicon particles as a multistage delivery system for imaging and therapeutic applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 151–157 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Martinez J. A. et al. highly efficient biocompatible single silicon nanowire electrodes with functional biological pore channels. Nano Lett. 9, 1121–1126 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Erogbogbo F. et al. In Vivo targeted cancer imaging, sentinel lymph node mapping and multi-channel imaging with biocompatible silicon nanocrystals. ACS Nano 5, 413–423 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Osminkina L. A. et al. Photoluminescent biocompatible silicon nanoparticles for cancer theranostic applications. J. Biophotonics 5, 529–535 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

