Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase protects the liver from inflammation and fibrosis by maintaining cholesterol homeostasis
- PMID: 27534992
- PMCID: PMC5036364
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M069807
Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase protects the liver from inflammation and fibrosis by maintaining cholesterol homeostasis
Abstract
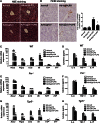
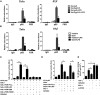
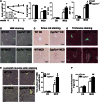
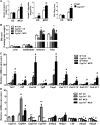
Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) plays a critical role in control of bile acid and cholesterol homeostasis. Bile acids activate farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5 (TGR5) to regulate lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. However, the role of bile acids in hepatic inflammation and fibrosis remains unclear. In this study, we showed that adenovirus-mediated overexpression of Cyp7a1 ameliorated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory cell infiltration and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in WT and TGR5-deficient (Tgr5-/-) mice, but not in FXR-deficient (Fxr-/-) mice, suggesting that bile acid signaling through FXR protects against hepatic inflammation. Nuclear factor κ light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB)-luciferase reporter assay showed that FXR agonists significantly inhibited TNF-α-induced NF-κB activity. Furthermore, chromatin immunoprecipitation and mammalian two-hybrid assays showed that ligand-activated FXR interacted with NF-κB and blocked recruitment of steroid receptor coactivator-1 to cytokine promoter and resulted in inhibition of NF-κB activity. Methionine/choline-deficient (MCD) diet increased hepatic inflammation, free cholesterol, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and fibrosis in CYP7A1-deficient (Cyp7a1-/-) mice compared with WT mice. Remarkably, adenovirus-mediated overexpression of Cyp7a1 effectively reduced hepatic free cholesterol and oxidative stress and reversed hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in MCD diet-fed Cyp7a1-/- mice. Current studies suggest that increased Cyp7a1 expression and bile acid synthesis ameliorate hepatic inflammation through activation of FXR, whereas reduced bile acid synthesis aggravates MCD diet-induced hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. Maintaining bile acid and cholesterol homeostasis is important for protecting against liver injury and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Keywords: Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5; bile acid; farnesoid X receptor; nuclear receptor.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deficiency of Both Farnesoid X Receptor and Takeda G Protein-Coupled Receptor 5 Exacerbated Liver Fibrosis in Mice.Hepatology. 2019 Sep;70(3):955-970. doi: 10.1002/hep.30513. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30664797 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase promotes hepatic bile acid synthesis and secretion and maintains cholesterol homeostasis.Hepatology. 2011 Mar;53(3):996-1006. doi: 10.1002/hep.24107. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21319191 Free PMC article.
-
Altered serotonin metabolism in Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5 knockout mice protects against diet-induced hepatic fibrosis.Liver Res. 2022 Dec 1;6(4):214-226. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2022.11.009. eCollection 2022 Dec. Liver Res. 2022. PMID: 39957909 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acid nuclear receptor FXR and digestive system diseases.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Mar;5(2):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Farnesoid X receptor, the bile acid sensing nuclear receptor, in liver regeneration.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Mar;5(2):93-8. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can diet modulate trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) production? What do we know so far?Eur J Nutr. 2021 Oct;60(7):3567-3584. doi: 10.1007/s00394-021-02491-6. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Eur J Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33533968 Review.
-
Hyperlipidemia Caused by Voriconazole: A Case Report.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Feb 10;14:483-487. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S301198. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 33603412 Free PMC article.
-
Farnesoid-X receptor as a therapeutic target for inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 6;13:1016836. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1016836. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36278234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of a Potent and Orally Active Dual GPBAR1/CysLT1R Modulator for the Treatment of Metabolic Fatty Liver Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 25;13:858137. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.858137. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35559268 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA MEG3 regulates the progress of osteoarthritis by regulating the miR-34a/Klotho axis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Apr;10(8):454. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-894. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35571440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trauner M., Fickert P., and Stauber R. E.. 1999. Inflammation-induced cholestasis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14: 946–959. - PubMed
-
- Greve J. W., Gouma D. J., and Buurman W. A.. 1989. Bile acids inhibit endotoxin-induced release of tumor necrosis factor by monocytes: an in vitro study. Hepatology. 10: 454–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

