Testing for ROS1 in non-small cell lung cancer: a review with recommendations
- PMID: 27535289
- PMCID: PMC5082594
- DOI: 10.1007/s00428-016-2000-3
Testing for ROS1 in non-small cell lung cancer: a review with recommendations
Abstract
Rearrangements of the ROS1 gene occur in 1-2 % of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs). Crizotinib, a highly effective inhibitor of ROS1 kinase activity, is now FDA-approved for the treatment of patients with advanced ROS1-positive NSCLC. Consequently, focus on ROS1 testing is growing. Most laboratories currently rely on fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) assays using a dual-colour break-apart probe to detect ROS1 rearrangements. Given the rarity of these rearrangements in NSCLC, detection of elevated ROS1 protein levels by immunohistochemistry may provide cost-effective screening prior to confirmatory FISH testing. Non-in situ testing approaches also hold potential as stand-alone methods or complementary tests, including multiplex real-time PCR assays and next-generation sequencing (NGS) platforms which include commercial test kits covering a range of fusion genes. In order to ensure high-quality biomarker testing, appropriate tissue handling, adequate control materials and participation in external quality assessment programmes are essential, irrespective of the testing technique employed. ROS1 testing is often only considered after negative tests for EGFR mutation and ALK gene rearrangement, based on the assumption that these oncogenic driver events tend to be exclusive. However, as the use of ROS1 inhibitors becomes routine, accurate and timely detection of ROS1 gene rearrangements will be critical for the optimal treatment of patients with NSCLC. As NGS techniques are introduced into routine diagnostic practice, ROS1 fusion gene testing will be provided as part of the initial testing package.
Keywords: Fluorescence in situ hybridisation; Immunohistochemistry; Non-small cell lung cancer; Predictive marker; ROS1; RT-PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards Conflicts of interest AR and GR have participated in advisory boards on behalf of Pfizer. FLR has received honoraria and research funding from Abbott, Pfizer and Roche. GR has participated in advisory boards on behalf of Pfizer and Qiagen. KK and LB have received honoraria from Pfizer. PP has received research grants and honoraria from Pfizer. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Figures
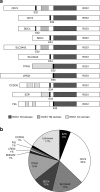

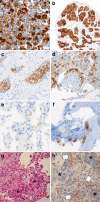
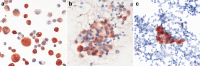
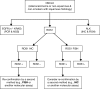
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, Longo F, Moran T, Insa A, De Marinis F, Corre R, Bover I, Illiano A, Dansin E, de Castro J, Milella M, Reguart N, Altavilla G, Jimenez U, Provencio M, Moreno MA, Terrasa J, Munoz-Langa J, Valdivia J, Isla D, Domine M, Molinier O, Mazieres J, Baize N, Garcia-Campelo R, Robinet G, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Lopez-Vivanco G, Gebbia V, Ferrera-Delgado L, Bombaron P, Bernabe R, Bearz A, Artal A, Cortesi E, Rolfo C, Sanchez-Ronco M, Drozdowskyj A, Queralt C, de Aguirre I, Ramirez JL, Sanchez JJ, Molina MA, Taron M, Paz-Ares L. Spanish Lung Cancer Group in collaboration with Groupe Francais de P-C, Associazione Italiana Oncologia T Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(3):239–246. - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K, Mekhail T, Felip E, Cappuzzo F, Paolini J, Usari T, Iyer S, Reisman A, Wilner KD, Tursi J, Blackhall F, Investigators P. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(23):2167–2177. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Forcione DG, Digumarthy SR, Iafrate AJ. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 21-2011. A 31-year-old man with ALK-positive adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(2):158–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

