A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis to Evaluate the Comparative Efficacy of Interventions for Unfit Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 27535291
- PMCID: PMC5055565
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-016-0398-2
A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis to Evaluate the Comparative Efficacy of Interventions for Unfit Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
Introduction: Rituximab plus fludarabine and cyclophosphamide (RFC) is the standard of care for fit patients with untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); however, its use is limited in 'unfit' (co-morbid and/or full-dose F-ineligible) patients due to its toxicity profile. We conducted a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis (NMA) to determine the relative efficacy of commercially available interventions for the first-line treatment of unfit CLL patients.
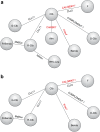
Methods: For inclusion in the NMA, studies had to be linked via common treatment comparators, report progression-free survival (PFS), and/or overall survival (OS), and meet at least one of the five inclusion criteria: median cumulative illness score >6, median creatinine clearance ≤70 mL/min, existing co-morbidities, median age ≥70 years, and no full-dose F in the comparator arm. A manual review, validated by external experts, of all studies that met at least one of these criteria was also performed to confirm that they evaluated first-line therapeutic options for unfit patients with CLL.
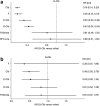
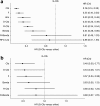
Results: In unfit patients, the main NMA (five studies for PFS and four for OS) demonstrated clear preference in terms of PFS for obinutuzumab + chlorambucil (G-Clb) versus rituximab + chlorambucil (R-Clb), ofatumumab + chlorambucil (O-Clb), fludarabine and chlorambucil (median hazard ratios [HRs] 0.43, 0.33, 0.20, and 0.19, respectively), and a trend for better efficacy versus rituximab + bendamustine (R-Benda) and RFC-Lite (median HR 0.81 and 0.88, respectively). OS results were generally consistent with PFS data, (median HR 0.48, 0.53, and 0.81, respectively) for G-Clb versus Clb, O-Clb, and R-Clb 0.35 and 0.81 versus F and R-Benda, respectively); however, the OS findings were associated with higher uncertainty. Treatment ranking reflected improved PFS and OS with G-Clb over other treatment strategies (median rank of one for both endpoints).
Conclusion: G-Clb is likely to show superior efficacy to other treatment options selected in our NMA for unfit treatment-naïve patients with CLL.
Funding: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Keywords: Bendamustine; Chlorambucil; Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; Co-morbidities; First-line; Fludarabine; Hematology; Network meta-analysis; Obinutuzumab; Oncology; Rituximab; Treatment-naïve.
Figures
References
-
- Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1164–1174. - PubMed
-
- Eichhorst B, Robak T, Montserrat E, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(suppl 5):v78–v84. - PubMed
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®). Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Version 1.2016. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp#site. Last accessed December, 2015.
-
- Knauf W, Re D. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: raising expectations in the treatment of elderly patients. J Leuk. 2015;3(2):1–8.
-
- Keating MJ, O’Brien S, Albitar M, et al. Early results of a chemoimmunotherapy regimen of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab as initial therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(18):4079–4088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

