Developmental restoration of LTP deficits in heterozygous CaMKIIα KO mice
- PMID: 27535377
- PMCID: PMC5102309
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00518.2016
Developmental restoration of LTP deficits in heterozygous CaMKIIα KO mice
Abstract
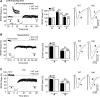
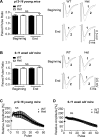
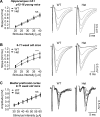
The Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) is a major mediator of long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD), two opposing forms of synaptic plasticity underlying learning, memory and cognition. The heterozygous CaMKIIα isoform KO (CaMKIIα+/-) mice have a schizophrenia-related phenotype, including impaired working memory. Here, we examined synaptic strength and plasticity in two brain areas implicated in working memory, hippocampus CA1 and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Young CaMKIIα+/- mice (postnatal days 12-16; corresponding to a developmental stage well before schizophrenia manifestation in humans) showed impaired hippocampal CA1 LTP. However, this LTP impairment normalized over development and was no longer detected in older CaMKIIα+/- mice (postnatal weeks 9-11; corresponding to young adults). By contrast, the CaMKIIα+/- mice failed to show the developmental increase of basal synaptic transmission in the CA1 seen in wild-type (WT) mice, resulting in impaired basal synaptic transmission in the older CaMKIIα+/- mice. Other electrophysiological parameters were normal, including mPFC basal transmission, LTP, and paired-pulse facilitation, as well as CA1 LTD, depotentiation, and paired-pulse facilitation at either age tested. Hippocampal CaMKIIα levels were ∼60% of WT in both the older CaMKIIα+/- mice and in the younger WT mice, resulting in ∼30% of adult WT expression in the younger CaMKIIα+/- mice; levels in frontal cortex were the same as in hippocampus. Thus, in young mice, ∼30% of adult CaMKIIα expression is sufficient for normal LTD and depotentiation, while normal LTP requires higher levels, with ∼60% of CaMKIIα expression sufficient for normal LTP in adult mice.
Keywords: CaMKII; LTD; LTP; schizophrenia; synaptic transmission.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Kinase-dead knock-in mouse reveals an essential role of kinase activity of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIalpha in dendritic spine enlargement, long-term potentiation, and learning.J Neurosci. 2009 Jun 10;29(23):7607-18. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0707-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19515929 Free PMC article.
-
Role of inhibitory autophosphorylation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (αCAMKII) in persistent (>24 h) hippocampal LTP and in LTD facilitated by novel object-place learning and recognition in mice.Behav Brain Res. 2015 May 15;285:79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.01.022. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 24480420
-
Age-related deficits in long-term potentiation are insensitive to hydrogen peroxide: coincidence with enhanced autophosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.J Neurosci Res. 2002 Nov 1;70(3):298-308. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10427. J Neurosci Res. 2002. PMID: 12391589
-
LTD, LTP, and the sliding threshold for long-term synaptic plasticity.Hippocampus. 1996;6(1):35-42. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:1<35::AID-HIPO7>3.0.CO;2-6. Hippocampus. 1996. PMID: 8878740 Review.
-
CaMKII: a molecular substrate for synaptic plasticity and memory.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014;122:61-87. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420170-5.00003-9. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014. PMID: 24484698 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of six CaMKIIα variants found in patients with schizophrenia.iScience. 2021 Sep 27;24(10):103184. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103184. eCollection 2021 Oct 22. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34667946 Free PMC article.
-
Young DAPK1 knockout mice have altered presynaptic function.J Neurophysiol. 2021 May 1;125(5):1973-1981. doi: 10.1152/jn.00055.2021. Epub 2021 Apr 21. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33881939 Free PMC article.
-
A revised view of the role of CaMKII in learning and memory.Nat Neurosci. 2025 Jan;28(1):24-34. doi: 10.1038/s41593-024-01809-x. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Nat Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39558039 Review.
-
Hippocampal-prefrontal theta coupling develops as mice become proficient in associative odorant discrimination learning.eNeuro. 2022 Sep 20;9(5):ENEURO.0259-22.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0259-22.2022. Online ahead of print. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 36127136 Free PMC article.
-
DAPK1 Mediates LTD by Making CaMKII/GluN2B Binding LTP Specific.Cell Rep. 2017 Jun 13;19(11):2231-2243. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.068. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28614711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson WW, Collingridge GL. The LTP Program: a data acquisition program for on-line analysis of long-term potentiation and other synaptic events. J Neurosci Methods 108: 71–83, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Bayer KU, Löhler J, Schulman H, Harbers K. Developmental expression of the CaM kinase II isoforms: ubiquitous gamma- and delta-CaM kinase II are the early isoforms and most abundant in the developing nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 70: 147–154, 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

