Isolation and characterization of vesicular and non-vesicular microRNAs circulating in sera of partially hepatectomized rats
- PMID: 27535708
- PMCID: PMC4989158
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31869
Isolation and characterization of vesicular and non-vesicular microRNAs circulating in sera of partially hepatectomized rats
Abstract
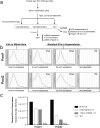
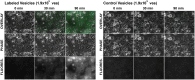
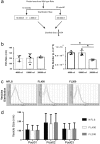
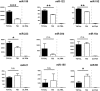
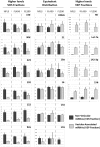
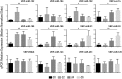
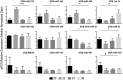
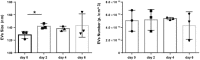
Circulating microRNAs are protected from degradation by their association with either vesicles or components of the RNAi machinery. Although increasing evidence indicates that cell-free microRNAs are transported in body fluids by different types of vesicles, current research mainly focuses on the characterization of exosome-associated microRNAs. However, as isolation and characterization of exosomes is challenging, it is yet unclear whether exosomes or other vesicular elements circulating in serum are the most reliable source for discovering disease-associated biomarkers. In this study, circulating microRNAs associated to the vesicular and non-vesicular fraction of sera isolated from partially hepatectomized rats were measured. Here we show that independently from their origin, levels of miR-122, miR-192, miR-194 and Let-7a are up-regulated two days after partial hepatectomy. The inflammation-associated miR-150 and miR-155 are up-regulated in the vesicular-fraction only, while the regeneration-associated miR-21 and miR-33 are up-regulated in the vesicular- and down-regulated in the non-vesicular fraction. Our study shows for the first time the modulation of non-vesicular microRNAs in animals recovering from partial hepatectomy, suggesting that, in the search for novel disease-associated biomarkers, the profiling of either vesicular or non-vesicular microRNAs may be more relevant than the analysis of microRNAs isolated from unfractionated serum.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammation Related MicroRNAs Are Modulated in Total Plasma and in Extracellular Vesicles from Rats with Chronic Ingestion of Sucrose.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2489479. doi: 10.1155/2016/2489479. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27999792 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Sep 8;18(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0753-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27608715 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA profiling in murine liver after partial hepatectomy.Int J Mol Med. 2012 May;29(5):747-55. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.902. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22307273
-
The prognostic and therapeutic application of microRNAs in breast cancer: Tissue and circulating microRNAs.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Feb;233(2):774-786. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25813. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28109133 Review.
-
Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as circulating biomarkers for breast cancer.Int J Cancer. 2016 Oct 1;139(7):1443-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30179. Epub 2016 May 31. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27170104 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Hepatobiliary Health and Disease.Compr Physiol. 2023 Jun 26;13(3):4631-4658. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c210046. Compr Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37358519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockout of microRNA-21 reduces biliary hyperplasia and liver fibrosis in cholestatic bile duct ligated mice.Lab Invest. 2016 Dec;96(12):1256-1267. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.112. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27775690 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating exosomal miRNAs as potential biomarkers for Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jun 14;26(22):2889-2901. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.2889. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32587437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective Isolation of Liver-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Redefines Performance of miRNA Biomarkers for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 17;10(1):195. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010195. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35052873 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic nucleic acid sensors of the innate immune system promote liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 16;8(1):12271. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29924-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30115978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chim S. S. et al.. Detection and Characterization of Placental MicroRNAs in Maternal Plasma. Clin Chem 54, 482–90 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Dimmeler S. & Zeiher A. M. Circulating microRNAs: novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases? European heart journal 31, 2705–7 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Gupta S. K., Bang C. & Thum T. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers and potential paracrine mediators of cardiovascular disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 3, 484–8 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Fichtlscherer S. et al.. Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation research 107, 677–84 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Neal C. S. et al.. Circulating microRNA expression is reduced in chronic kidney disease. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation: official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association 26, 3794–802 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

