MASP-3 is the exclusive pro-factor D activator in resting blood: the lectin and the alternative complement pathways are fundamentally linked
- PMID: 27535802
- PMCID: PMC4989169
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31877
MASP-3 is the exclusive pro-factor D activator in resting blood: the lectin and the alternative complement pathways are fundamentally linked
Abstract
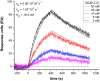
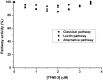
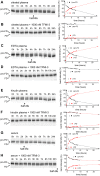
MASP-3 was discovered 15 years ago as the third mannan-binding lectin (MBL)-associated serine protease of the complement lectin pathway. Lacking any verified substrate its role remained ambiguous. MASP-3 was shown to compete with a key lectin pathway enzyme MASP-2 for MBL binding, and was therefore considered to be a negative complement regulator. Later, knock-out mice experiments suggested that MASP-1 and/or MASP-3 play important roles in complement pro-factor D (pro-FD) maturation. However, studies on a MASP-1/MASP-3-deficient human patient produced contradicting results. In normal resting blood unperturbed by ongoing coagulation or complement activation, factor D is present predominantly in its active form, suggesting that resting blood contains at least one pro-FD activating proteinase that is not a direct initiator of coagulation or complement activation. We have recently showed that all three MASPs can activate pro-FD in vitro. In resting blood, however, using our previously evolved MASP-1 and MASP-2 inhibitors we proved that neither MASP-1 nor MASP-2 activates pro-FD. Other plasma proteinases, particularly MASP-3, remained candidates for that function. For this study we evolved a specific MASP-3 inhibitor and unambiguously proved that activated MASP-3 is the exclusive pro-FD activator in resting blood, which demonstrates a fundamental link between the lectin and alternative pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Gaboriaud C., Teillet F., Gregory L. A., Thielens N. M. & Arlaud G. J. Assembly of C1 and the MBL- and ficolin-MASP complexes: Structural insights. Immunobiology 212, 279–288 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

