A microbial sensor for organophosphate hydrolysis exploiting an engineered specificity switch in a transcription factor
- PMID: 27536006
- PMCID: PMC5041483
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw687
A microbial sensor for organophosphate hydrolysis exploiting an engineered specificity switch in a transcription factor
Abstract
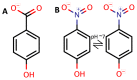
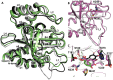
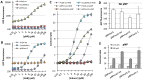
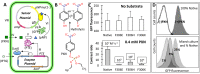
A whole-cell biosensor utilizing a transcription factor (TF) is an effective tool for sensitive and selective detection of specialty chemicals or anthropogenic molecules, but requires access to an expanded repertoire of TFs. Using homology modeling and ligand docking for binding pocket identification, assisted by conservative mutations in the pocket, we engineered a novel specificity in an Acinetobacter TF, PobR, to 'sense' a chemical p-nitrophenol (pNP) and measured the response via a fluorescent protein reporter expressed from a PobR promoter. Out of 10(7) variants of PobR, four were active when dosed with pNP, with two mutants showing a specificity switch from the native effector 4-hydroxybenzoate (4HB). One of the mutants, pNPmut1 was then used to create a smart microbial cell responding to pNP production from hydrolysis of an insecticide, paraoxon, in a coupled assay involving phosphotriesterase (PTE) enzyme expressed from a separate promoter. We show the fluorescence of the cells correlated with the catalytic efficiency of the PTE variant expressed in each cell. High selectivity between similar molecules (4HB versus pNP), high sensitivity for pNP detection (∼2 μM) and agreement of apo- and holo-structures of PobR scaffold with predetermined computational models are other significant results presented in this work.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research 2016. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rosetta comparative modeling for library design: Engineering alternative inducer specificity in a transcription factor.Proteins. 2015 Jul;83(7):1327-40. doi: 10.1002/prot.24828. Epub 2015 May 29. Proteins. 2015. PMID: 25974100
-
Development of a yeast biosensor-biocatalyst for the detection and biodegradation of the organophosphate paraoxon.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Oct;76(6):1383-94. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-1107-5. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17665192
-
Cell surface display of organophosphorus hydrolase for sensitive spectrophotometric detection of p-nitrophenol substituted organophosphates.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2014 Feb 5;55:107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Oct 27. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2014. PMID: 24411452
-
Detoxification of organophosphate nerve agents by bacterial phosphotriesterase.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005 Sep 1;207(2 Suppl):459-70. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.02.025. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15982683 Review.
-
Converting a Periplasmic Binding Protein into a Synthetic Biosensing Switch through Domain Insertion.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jan 3;2019:4798793. doi: 10.1155/2019/4798793. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30719443 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Directed evolution of the PcaV allosteric transcription factor to generate a biosensor for aromatic aldehydes.J Biol Eng. 2019 Nov 27;13:91. doi: 10.1186/s13036-019-0214-z. eCollection 2019. J Biol Eng. 2019. PMID: 31798685 Free PMC article.
-
A Microbial Electrochemical Technology to Detect and Degrade Organophosphate Pesticides.ACS Cent Sci. 2021 Oct 27;7(10):1718-1727. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00931. Epub 2021 Sep 21. ACS Cent Sci. 2021. PMID: 34729415 Free PMC article.
-
When synthetic biology meets medicine.Life Med. 2024 Mar 6;3(1):lnae010. doi: 10.1093/lifemedi/lnae010. eCollection 2024 Feb. Life Med. 2024. PMID: 39872399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Directed Evolution of Transcription Factor-Based Biosensors for Altered Effector Specificity.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2461:175-193. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2152-3_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35727451
-
Precise Genomic Riboregulator Control of Metabolic Flux in Microbial Systems.ACS Synth Biol. 2022 Oct 21;11(10):3216-3227. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00638. Epub 2022 Sep 21. ACS Synth Biol. 2022. PMID: 36130255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eggeling L., Bott M., Marienhagen J. Novel screening methods—biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015;35:30–36. - PubMed
-
- Tang S.-Y., Qian S., Akinterinwa O., Frei C.S., Gredell J.A., Cirino P.C. Screening for enhanced triacetic acid lactone production by recombinant Escherichia coli expressing a designed triacetic acid lactone reporter. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;135:10099–10103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

