Update and new approaches in the treatment of Castleman disease
- PMID: 27536166
- PMCID: PMC4976903
- DOI: 10.2147/JBM.S60514
Update and new approaches in the treatment of Castleman disease
Abstract
First described 60 years ago, Castleman disease comprises a rare and heterogeneous cluster of disorders, characterized by lymphadenopathy with unique histological features and associated with cytokine-driven constitutional symptoms and biochemical disturbances. Although unicentric Castleman disease is curable with complete surgical excision, its multicentric counterpart is a considerable therapeutic challenge. The recent development of biological agents, particularly monoclonal antibodies to interleukin-6 and its receptor, allow for more targeted disease-specific intervention that promises improved response rates and more durable disease control; however, further work is required to fill knowledge gaps in terms of underlying pathophysiology and to facilitate alternative treatment options for refractory cases.
Keywords: Castleman disease; angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia; biologics; rituximab; siltuximab; tocilizumab.
Figures
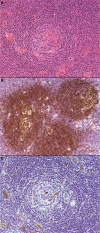
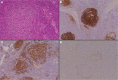
References
-
- Case records of the Massachusetts general hospital weekly clinicopathological exercises: case 40011. N Engl J Med. 1954;250(1):26–30. - PubMed
-
- Munshi N, Mehra M, van de Velde H, Desai A, Potluri R, Vermeulen J. Use of a claims database to characterize and estimate the incidence rate for Castleman disease. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(5):1252–1260. - PubMed
-
- Powles T, Stebbing J, Bazeos A, et al. The role of immune suppression and HHV-8 in the increasing incidence of HIV-associated multicentric Castleman’s disease. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(4):775–779. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

