Effects of chlorhexidine, essential oils and herbal medicines (Salvia, Chamomile, Calendula) on human fibroblast in vitro
- PMID: 27536196
- PMCID: PMC4967643
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2016.59739
Effects of chlorhexidine, essential oils and herbal medicines (Salvia, Chamomile, Calendula) on human fibroblast in vitro
Abstract
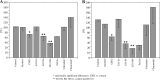
Antiseptic rinses have been successfully used in inflammatory states of the gums and oral cavity mucosa. Antibacterial effects of chlorhexidine, essential oils and some herbs are well documented. Reaction of host tissue to these substances has much poorer documentation. The aim of the study was to analyse the influence of chlorhexidine (CHX), essential oil (EO: thymol, 0.064%; eucalyptol, 0.092%; methyl salicylate, 0.060%; menthol, 0.042%) mouth rinses and salvia, chamomile and calendula brews on fibroblast biology in vitro. The human fibroblast CCD16 line cells were cultured in incubation media which contained the examined substances. After 24 and 48 hours, the cell morphology, relative growth and apoptosis were evaluated. Exposure of fibroblasts to CHX, EO or salvia caused various changes in cell morphology. Cells cultured for 48 hours with CHX revealed a noticeably elongated shape of while cells cultured in high EO concentration or with salvia were considerably smaller and contracted with fewer projections. Chlorhexidine, EO and salvia reduced the fibroblast proliferation rate and stimulated cell death. Both reactions to EO were dose dependent. Cells exposure to chamomile or calendula brews did not change morphology or proliferation of fibroblasts. The results of this in vitro study showed that in contrast to chamomile and calendula, the brews of EO, CHX or salvia had a negative influence on fibroblast biology.
Keywords: chlorhexidine; essential oils; fibroblast; herbs; morphology; mouth rinses; proliferation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of essential oil and chlorhexidine mouthwashes on gingival fibroblast survival and migration.J Periodontol. 2013 Aug;84(8):1211-20. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.120312. Epub 2012 Oct 29. J Periodontol. 2013. PMID: 23106509
-
In vitro comparison of zinc-based, chlorhexidine, and essential oil mouth rinses.J Periodontol. 2025 May;96(5):429-439. doi: 10.1002/JPER.23-0619. Epub 2024 Jul 16. J Periodontol. 2025. PMID: 39012314
-
Cytotoxicity of three commercial mouthrinses on extracellular matrix metabolism and human gingival cell behaviour.Toxicol In Vitro. 2016 Aug;34:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2016.03.015. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Toxicol In Vitro. 2016. PMID: 27039991
-
Antiseptic mouth rinses: an update on comparative effectiveness, risks and recommendations.J Dent Hyg. 2013 Feb;87(1):10-8. Epub 2013 Feb 5. J Dent Hyg. 2013. PMID: 23433693 Review.
-
Efficacy of chlorhexidine rinses after periodontal or implant surgery: a systematic review.Clin Oral Investig. 2019 Jan;23(1):21-32. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2761-y. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Clin Oral Investig. 2019. PMID: 30535817
Cited by
-
Proliferation and In Vitro Wound Healing Effects of the Microniosomes Containing Narcissus tazetta L. Bulb Extract on Primary Human Fibroblasts (HDFs).Daru. 2018 Sep 12;26(1):31-42. doi: 10.1007/s40199-018-0211-7. Online ahead of print. Daru. 2018. PMID: 30209758 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Electrospun Polycaprolactone-Based Wound Dressings: An In Vitro Study About the Importance of the Direct Contact to Elicit Bactericidal Activity.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2019 Sep 1;8(9):438-451. doi: 10.1089/wound.2018.0893. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2019. PMID: 31737424 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities of two components of Cymbopogon citratus essential oil.J Clin Exp Dent. 2020 Aug 1;12(8):e749-e754. doi: 10.4317/jced.56863. eCollection 2020 Aug. J Clin Exp Dent. 2020. PMID: 32913572 Free PMC article.
-
Can components of the plasminogen activation system predict the outcome of kidney transplants?Cent Eur J Immunol. 2018;43(2):222-230. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2018.77394. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30135637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the Impact of Ethanol Extract of Calendula officinalis L. on Human Fibroblast Cell Cultures Using the PANsys 3000 Device for Breeding and Visualization of Cells.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 22;13(10):1949. doi: 10.3390/life13101949. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cochran DL. Inflammation and bone loss in periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 2008;79:1569–1576. - PubMed
-
- Forabosco A, Spinato S, Grandi T, et al. A comparative study between different techniques in non-surgical periodontal treatment. Minerva Stomatol. 2006;55:289–296. - PubMed
-
- Lang NP, Tan WC, Krahenmann MA, et al. A systematic review of the effects of full-mouth debridment with and without antiseptics in patients with chronic periodontitis. JClin Periodontol. 2008;35:8–21. - PubMed
-
- Haffajee AD, Roberts C, Murray L, et al. Effect of herbal, essential oil, and chlorhexidine mouthrinses on the composition of the subgingival microbiota and clinical periodontal parameters. J Clin Dent. 2009;20:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Haffajee AD, Yaskell T, Socransky SS. Antimicrobial effectiveness of an herbal mouthrinse compared with an essential oil and a chlorhexidine mouthrinse. J Am Dent Assoc. 2008;139:606–611. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
