Identification of metabolites of dalfampridine (4-aminopyridine) in dog and rat
- PMID: 27536440
- PMCID: PMC4937651
- DOI: 10.3109/21556660.2013.794143
Identification of metabolites of dalfampridine (4-aminopyridine) in dog and rat
Abstract
Background: Dalfampridine (4-aminopyridine; 4-AP) is a potassium channel blocker available in the United States to improve walking in patients with multiple sclerosis as demonstrated by an increase in walking speed. Its pharmacokinetics have been evaluated in human studies but its metabolites are not well characterized. This study characterizes the metabolic profile of dalfampridine in two animal species that were used to support nonclinical toxicology evaluation.
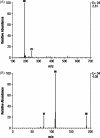
Methods: Metabolic profiling of single oral (14)C-4-AP doses was performed in 12 adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. Similarly, metabolic profiling was performed in beagle dogs in two studies that administered (14)C-4-AP by gastric intubation; the first study included six animals (three males, three females), and the second study included two animals (one male, one female). Blood and urine samples were evaluated using high performance liquid chromatography, thin layer chromatography, and radioanalysis (liquid scintillation counting), with further identification of components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry.
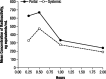
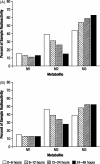
Results: Five radioactive components, M1-M5, were detected in rat plasma, although most of the radioactivity corresponded with unchanged 4-AP. Based on Rf values, M1 and M2 coseparated with reference standards of 3-hydroxy-4-AP and 4-AP, respectively. Additionally, components M1, M2, and M3 coseparated with the same components isolated from the urine of a dog dosed with (14)C-4-AP and identified as 3-hydroxy-4-AP, 4-AP, and 3-hydroxy-4-AP sulfate, respectively; M4 and M5 could not be identified because of low concentrations. In dogs, most of the radioactivity was excreted within the first 24 hours as unchanged compound.
Conclusions: Following oral dosing, 4-AP was rapidly absorbed in rats and dogs, with rapid excretion and almost complete urinary recovery in dogs. The primary metabolites in both animal models were 3-hydroxy-4-AP and 3-hydroxy-4-AP sulfate. Systemic clearance not accounted for by renal excretion of 4-AP may occur by liver metabolism by hydroxylation of 4-AP to 3-hydroxy-4-AP followed by sulfate conjugation to 3-hydroxy-4-AP sulfate.
Keywords: 4-aminopyridine; Dalfampridine; Dog; Metabolites; Preclinical models; Rat.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of metabolites of dalfampridine (4-aminopyridine) in human subjects and reaction phenotyping of relevant cytochrome P450 pathways.J Drug Assess. 2013 Aug 14;2(1):117-26. doi: 10.3109/21556660.2013.833099. eCollection 2013. J Drug Assess. 2013. PMID: 27536445 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dalfampridine and its metabolites on cloned human potassium channels Kv 1.1, Kv 1.2, and Kv 1.4 expressed in human embryonic kidney cells.J Drug Assess. 2013 Apr 2;2(1):58-66. doi: 10.3109/21556660.2013.791623. eCollection 2013. J Drug Assess. 2013. PMID: 27536438 Free PMC article.
-
[Biotransformation of tramadol in man and animal (author's transl)].Arzneimittelforschung. 1981;31(11):1932-43. Arzneimittelforschung. 1981. PMID: 7198474 German.
-
Dalfampridine: a new agent for symptomatic management of multiple sclerosis.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2011 Dec 15;68(24):2335-40. doi: 10.2146/ajhp110134. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2011. PMID: 22135060 Review.
-
The safety profile of dalfampridine extended release in multiple sclerosis clinical trials.Clin Ther. 2012 May;34(5):1056-69. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Clin Ther. 2012. PMID: 22497693 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Stability of the Demyelination Positron Emission Tomography Tracer [18F]3-Fluoro-4-Aminopyridine and Identification of Its Metabolites.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2023 Jul;386(1):93-101. doi: 10.1124/jpet.122.001462. Epub 2023 Apr 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2023. PMID: 37024145 Free PMC article.
-
Common anesthetic used in preclinical PET imaging inhibits metabolism of the PET tracer [18F]3F4AP.J Neurochem. 2024 Sep;168(9):2577-2586. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16118. Epub 2024 May 1. J Neurochem. 2024. PMID: 38690718 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of metabolites of dalfampridine (4-aminopyridine) in human subjects and reaction phenotyping of relevant cytochrome P450 pathways.J Drug Assess. 2013 Aug 14;2(1):117-26. doi: 10.3109/21556660.2013.833099. eCollection 2013. J Drug Assess. 2013. PMID: 27536445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ampyra® (dalfampridine) extended release tablets [package insert]. Ardsley, NY, USA: Acorda Therapeutics Inc., 2011
-
- Goodman AD Brown TR Krupp L et al. Sustained release of oral fampridine in multiple sclerosis: a randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 2009;373:732-8 - PubMed
-
- Goodman AD Brown TR Edwards KR et al. A phase 3 trial of extended release oral dalfampridine in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2010;68:494-502 - PubMed
-
- Dunn J, Blight A. Dalfampridine: a brief review of its mechanism of action and efficacy as a treatment to improve walking in patients with multiple sclerosis. Curr Med Res Opin 2011;27:1415-23 - PubMed
-
- Targ EF, Kocsis JD. 4-Aminopyridine leads to restoration of conduction in demyelinated rat sciatic nerve. Brain Res 1985;328:358-61 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
