Modulation of Host miRNAs by Intracellular Bacterial Pathogens
- PMID: 27536558
- PMCID: PMC4971075
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00079
Modulation of Host miRNAs by Intracellular Bacterial Pathogens
Abstract
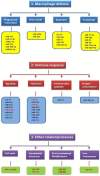
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs that regulate the expression of protein coding genes of viruses and eukaryotes at the post-transcriptional level. The eukaryotic genes regulated by miRNAs include those whose products are critical for biological processes such as cell proliferation, metabolic pathways, immune response, and development. It is now increasingly recognized that modulation of miRNAs associated with biological processes is one of the strategies adopted by bacterial pathogens to survive inside host cells. In this review, we present an overview of the recent findings on alterations of miRNAs in the host cells by facultative intracellular bacterial pathogens. In addition, we discuss how the altered miRNAs help in the survival of these pathogens in the intracellular environment.
Keywords: Francisella; Listeria; Mycobacterium; Salmonella; host; macrophages; microRNA; regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The mammalian microRNA response to bacterial infections.RNA Biol. 2012 Jun;9(6):742-50. doi: 10.4161/rna.20018. Epub 2012 Jun 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22664920 Review.
-
Mammalian microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in the host-bacterial pathogen crosstalk.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 May;65:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.06.016. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27381344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and bacterial infection.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Sep;15(9):1496-507. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12159. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23795564 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in the regulation of immune response against infections.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013 Jan;14(1):1-7. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1200292. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013. PMID: 23303626 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs at the Host-Bacteria Interface: Host Defense or Bacterial Offense.Trends Microbiol. 2019 Mar;27(3):206-218. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.10.011. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Trends Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30477908 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of Rickettsial Diseases: Pathogenic and Immune Mechanisms of an Endotheliotropic Infection.Annu Rev Pathol. 2019 Jan 24;14:127-152. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012800. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Annu Rev Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30148688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis induces differential cytosine methylation at miR-21 transcription start site region.Iran J Vet Res. 2018 Fall;19(4):262-269. Iran J Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 30774666 Free PMC article.
-
A Long Journey Ahead: Long Non-coding RNAs in Bacterial Infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Mar 28;7:95. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00095. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28401065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The current landscape of microRNAs (miRNAs) in bacterial pneumonia: opportunities and challenges.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Aug 19;27(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00368-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35986232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Identification of Two DNA Methyltransferase Genes and Their Functional Characterization in the Anti-Bacterial Immunity of Antheraea pernyi.Front Immunol. 2022 May 16;13:855888. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.855888. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35651618 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

