Surgical Treatment of Undisplaced Femur Neck Fractures in Dementia Patients Using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation
- PMID: 27536620
- PMCID: PMC4972721
- DOI: 10.5371/hp.2015.27.3.164
Surgical Treatment of Undisplaced Femur Neck Fractures in Dementia Patients Using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation
Abstract
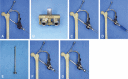
Purpose: People with dementia have poor mobility and discharge outcomes following hip fractures. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiological results of internal fixation of undisplaced femur neck fractures (Garden types 1 and 2) by proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in dementia patients.
Materials and methods: We studied retrospectively 19 patients with undisplaced femur neck fracture. All patients were over 70 years of age, walked independently with a cane or crutches and suffered moderate-to-severe dementia. Patients were treated with PFNA and followed-up for more than 2 years. Revision, loss of fixation, complications, and walking ability outcomes were measured.
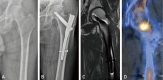
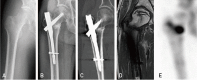
Results: In walking-ability evaluation, patients showed an average decrease of just 0.2 points at the final follow-up. Walking ability was evaluated from before injury to 4 weeks after surgery and decreased by less than 0.5 points. Radiological bone union was achieved in 17 cases; the average time to bone union was 4.14 months (range, 2.5-7 months). Complications included non-union in two cases and femoral head avascular necrosis in one case of non-union.
Conclusion: We found that for patients with osteoporotic bone tissues in their femoral heads or patients (e.g., those suffering dementia) for whom cooperating with medical workers for postoperative walking control or rehabilitation exercises is difficult, implanting a mechanically stable spiral blade for fixation of femoral neck fractures could facilitate walking after surgery.
Keywords: Dementia; Proximal femoral nail antirotation; Undisplaced femoral neck fracture.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiographic and functional results of osteosynthesis using the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010;44(2):127-34. doi: 10.3944/AOTT.2010.2237. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010. PMID: 20676015
-
[Comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation and reconstruction nail for ipsilateral fractures of hip and femoral shaft].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Aug;26(8):905-9. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23012919 Chinese.
-
Mid-term outcomes after intramedullary fixation of peritrochanteric femoral fractures using the new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA).Injury. 2010 Aug;41(8):810-7. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.03.020. Epub 2010 May 15. Injury. 2010. PMID: 20472234
-
[Ipsilateral fractures of the proximal femur and the femoral shaft].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010 Oct;77(5):378-88. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010. PMID: 21040649 Czech.
-
Cancellous screw fixation for undisplaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2014 Dec;22(3):282-6. doi: 10.1177/230949901402200303. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2014. PMID: 25550003
Cited by
-
Treatment of Traumatic Femoral Neck Fractures with an Intramedullary Nail in Osteoporotic Bones.Indian J Orthop. 2021 Mar 11;55(3):621-628. doi: 10.1007/s43465-020-00292-3. eCollection 2021 Jun. Indian J Orthop. 2021. PMID: 33995865 Free PMC article.
-
Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation II (PFNA II): technical note and cases series.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Jan 20;15(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1524-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 31959205 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical options for improving the ipsilateral femoral neck, shaft, and distal femoral fracture: A case report and literature review.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Mar;116:109367. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.109367. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38401321 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term results after over 17 years - Intramedullary gliding nail as treatment for traumatic femoral neck fractures.J Orthop. 2021 May 27;26:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2021.05.029. eCollection 2021 Jul-Aug. J Orthop. 2021. PMID: 34140760 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of the Clinicoradiological Outcomes of Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated Using Proximal Femoral Nail and Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation.Cureus. 2024 May 19;16(5):e60639. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60639. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38903304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garden RS. Stability and union in subcapital fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1964;46:630–647. - PubMed
-
- Gjertsen JE, Engesaeter LB, Furnes O, et al. The Norwegian Hip Fracture Register: experiences after the first 2 years and 15,576 reported operations. Acta Orthop. 2008;79:583–593. - PubMed
-
- Rogmark C, Flensburg L, Fredin H. Undisplaced femoral neck fractures--no problems? A consecutive study of 224 patients treated with internal fixation. Injury. 2009;40:274–276. - PubMed
-
- Leighton RK, Schmidt AH, Collier P, Trask K. Advances in the treatment of intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly. Injury. 2007;38(Suppl 3):S24–S34. - PubMed
-
- Lin D, Lian K, Ding Z, Zhai W, Hong J. Proximal femoral locking plate with cannulated screws for the treatment of femoral neck fractures. Orthopedics. 2012;35:e1–e5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

