Stochastic and deterministic dynamics of intrinsically irregular firing in cortical inhibitory interneurons
- PMID: 27536875
- PMCID: PMC5030087
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.16475
Stochastic and deterministic dynamics of intrinsically irregular firing in cortical inhibitory interneurons
Abstract
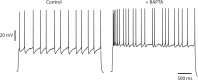
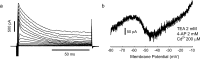
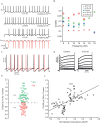
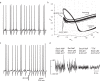
Most cortical neurons fire regularly when excited by a constant stimulus. In contrast, irregular-spiking (IS) interneurons are remarkable for the intrinsic variability of their spike timing, which can synchronize amongst IS cells via specific gap junctions. Here, we have studied the biophysical mechanisms of this irregular spiking in mice, and how IS cells fire in the context of synchronous network oscillations. Using patch-clamp recordings, artificial dynamic conductance injection, pharmacological analysis and computational modeling, we show that spike time irregularity is generated by a nonlinear dynamical interaction of voltage-dependent sodium and fast-inactivating potassium channels just below spike threshold, amplifying channel noise. This active irregularity may help IS cells synchronize with each other at gamma range frequencies, while resisting synchronization to lower input frequencies.
Keywords: computational biology; cortical interneuron; mouse; neuroscience; spiking irregularity; systems biology; voltage-gated potassium conductance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





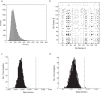
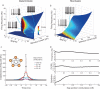

Similar articles
-
Integration of broadband conductance input in rat somatosensory cortical inhibitory interneurons: an inhibition-controlled switch between intrinsic and input-driven spiking in fast-spiking cells.J Neurophysiol. 2009 Feb;101(2):1056-72. doi: 10.1152/jn.91057.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 17. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19091918
-
Origin of intrinsic irregular firing in cortical interneurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 7;110(19):7886-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305219110. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23610409 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Mechanisms of Tight Spike Synchrony at Gamma Frequency in Cerebral Cortex.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;35(28):10236-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0828-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26180200 Free PMC article.
-
Irregular firing of isolated cortical interneurons in vitro driven by intrinsic stochastic mechanisms.Neural Comput. 2008 Jan;20(1):44-64. doi: 10.1162/neco.2008.20.1.44. Neural Comput. 2008. PMID: 18045000 Free PMC article.
-
Kv4.2 channel activity controls intrinsic firing dynamics of arcuate kisspeptin neurons.J Physiol. 2018 Mar 1;596(5):885-899. doi: 10.1113/JP274474. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29214635 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cortical reliability amid noise and chaos.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 22;10(1):3792. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11633-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31439838 Free PMC article.
-
Kv4 channels to kisspeptin neurons: 'Let's (not) go steady'.J Physiol. 2018 Mar 1;596(5):757-758. doi: 10.1113/JP275673. Epub 2018 Jan 24. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29331017 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A dopamine gradient controls access to distributed working memory in the large-scale monkey cortex.Neuron. 2021 Nov 3;109(21):3500-3520.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.08.024. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Neuron. 2021. PMID: 34536352 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic unpredictable stress induces depression-related behaviors by suppressing AgRP neuron activity.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Jun;26(6):2299-2315. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-01004-x. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33432188 Free PMC article.
-
Learning interpretable dynamics of stochastic complex systems from experimental data.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 17;15(1):6029. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50378-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39019850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso A, Klink R. Differential electroresponsiveness of stellate and pyramidal-like cells of medial entorhinal cortex layer II. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1993;70:128–143. - PubMed
-
- Alonso G, Widmer H. Clustering of KV4.2 potassium channels in postsynaptic membrane of rat supraoptic neurons: an ultrastructural study. Neuroscience. 1997;77:617–621. - PubMed
-
- Amarillo Y, De Santiago-Castillo JA, Dougherty K, Maffie J, Kwon E, Covarrubias M, Rudy B. Ternary Kv4.2 channels recapitulate voltage-dependent inactivation kinetics of A-type K+ channels in cerebellar granule neurons. Journal of Physiology. 2008;586:2093–2106. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.150540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ascoli GA, Alonso-Nanclares L, Anderson SA, Barrionuevo G, Benavides-Piccione R, Burkhalter A, Buzsáki G, Cauli B, Defelipe J, Fairén A, Feldmeyer D, Fishell G, Fregnac Y, Freund TF, Gardner D, Gardner EP, Goldberg JH, Helmstaedter M, Hestrin S, Karube F, Kisvárday ZF, Lambolez B, Lewis DA, Marin O, Markram H, Muñoz A, Packer A, Petersen CC, Rockland KS, Rossier J, Rudy B, Somogyi P, Staiger JF, Tamas G, Thomson AM, Toledo-Rodriguez M, Wang Y, West DC, Yuste R, Petilla Interneuron Nomenclature Group Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2008;9:557–568. doi: 10.1038/nrn2402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

