Molecular mechanisms linking geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase to cell survival and proliferation
- PMID: 27537059
- PMCID: PMC5532733
- DOI: 10.1080/09687688.2016.1213432
Molecular mechanisms linking geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase to cell survival and proliferation
Abstract
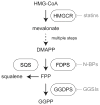
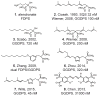
Geranylgeranyl diphosphate is a 20-carbon isoprenoid phospholipid whose lipid moiety can be post-translationally incorporated into proteins to promote membrane association. The process of geranylgeranylation has been implicated in anti-proliferative effects of clinical agents that inhibit enzymes of the mevalonate pathway (i.e. statins and nitrogenous bisphosphonates) as well as experimental agents that deplete geranylgeranyl diphosphate. Inhibitors of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase are an attractive way to block geranylgeranylation because they possess a calcium-chelating substructure to allow localization to bone and take advantage of a unique position of the enzyme within the biosynthetic pathway. Here, we describe recent advances in geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase expression and inhibitor development with a particular focus on the molecular mechanisms that link geranylgeranyl diphosphate to cell proliferation via geranylgeranylated small GTPases.
Keywords: Bisphosphonates; GGDPS; Rac; Ras; Rho; small GTPase.
Conflict of interest statement
Compound
Figures


References
-
- Allal C, Favre G, Couderc B, Salicio S, Sixou S, Hamilton AD, Sebti SM, Lajoie-Mazenc I, Pradines A. Rhoa prenylation is required for promotion of cell growth and transformation and cytoskeleton organization but not for induction of serum response element transcription. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:31001–8. - PubMed
-
- Allal C, Pradines A, Hamilton AD, Sebti SM, Favre G. Farnesylated rhob prevents cell cycle arrest and actin cytoskeleton disruption caused by the geranylgeranyltransferase i inhibitor ggti-298. Cell cycle. 2002;1:430–7. - PubMed
-
- Amin D, Cornell SA, Gustafson SK, Needle SJ, Ullrich JW, Bilder GE, Perrone MH. Bisphosphonates used for the treatment of bone disorders inhibit squalene synthase and cholesterol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res. 1992;33:1657–1663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
