Engineered Microvessels for the Study of Human Disease
- PMID: 27537085
- PMCID: PMC5125325
- DOI: 10.1115/1.4034428
Engineered Microvessels for the Study of Human Disease
Abstract
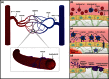
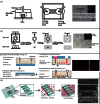
The microvasculature is an extensive, heterogeneous, and complex system that plays a critical role in human physiology and disease. It nourishes almost all living human cells and maintains a local microenvironment that is vital for tissue and organ function. Operating under a state of continuous flow, with an intricate architecture despite its small caliber, and subject to a multitude of biophysical and biochemical stimuli, the microvasculature can be a complex subject to study in the laboratory setting. Engineered microvessels provide an ideal platform that recapitulates essential elements of in vivo physiology and allows study of the microvasculature in a precise and reproducible way. Here, we review relevant structural and functional vascular biology, discuss different methods to engineer microvessels, and explore the applications of this exciting tool for the study of human disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oriented matrix promotes directional tubulogenesis.Acta Biomater. 2015 Jan;11:264-73. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.08.037. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 25219769 Free PMC article.
-
Direct 3D bioprinting of prevascularized tissue constructs with complex microarchitecture.Biomaterials. 2017 Apr;124:106-115. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.042. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28192772 Free PMC article.
-
Novel method to improve vascularization of tissue engineered constructs with biodegradable fibers.Biofabrication. 2016 Jan 7;8(1):015004. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/8/1/015004. Biofabrication. 2016. PMID: 26741237
-
Vascularization in bone tissue engineering: physiology, current strategies, major hurdles and future challenges.Macromol Biosci. 2010 Jan 11;10(1):12-27. doi: 10.1002/mabi.200900107. Macromol Biosci. 2010. PMID: 19688722 Review.
-
Engineered Liver Platforms for Different Phases of Drug Development.Trends Biotechnol. 2017 Feb;35(2):172-183. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Trends Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27592803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue-Engineered Microvessels: A Review of Current Engineering Strategies and Applications.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Aug;13(21):e2303419. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303419. Epub 2024 May 9. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38686434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microvascular Function and Exercise Training: Functional Implication of Nitric Oxide Signaling and Ion Channels.Pulse (Basel). 2024 Mar 12;12(1):27-33. doi: 10.1159/000538271. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Pulse (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38572498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ebola Hemorrhagic Shock Syndrome-on-a-Chip.iScience. 2020 Jan 24;23(1):100765. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.100765. Epub 2019 Dec 12. iScience. 2020. PMID: 31887664 Free PMC article.
-
Vascularity and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Front Radiol. 2021 Dec 9;1:735567. doi: 10.3389/fradi.2021.735567. eCollection 2021. Front Radiol. 2021. PMID: 37492179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascularized Microfluidics and Their Untapped Potential for Discovery in Diseases of the Microvasculature.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2021 Jul 13;23:407-432. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-091520-025358. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 33863238 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ross, M. H. , and Pawlina, W. , 2006, Histology: A Text and Atlas: With Correlated Cell and Molecular Biology, Lippincott Wiliams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

