Thiamin Diphosphate Activation in 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-Phosphate Synthase: Insights into the Mechanism and Underlying Intermolecular Interactions
- PMID: 27537621
- PMCID: PMC5379999
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b07248
Thiamin Diphosphate Activation in 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-Phosphate Synthase: Insights into the Mechanism and Underlying Intermolecular Interactions
Abstract
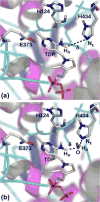
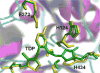
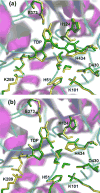
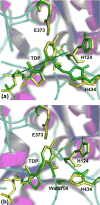
1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS) is a thiamin diphosphate (TDP) dependent enzyme that marks the beginning of the methylerythritol 4-phosphate isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. The mechanism of action for DXS is still poorly understood and begins with the formation of a thiazolium ylide. This TDP activation step is thought to proceed through an intramolecular deprotonation by the 4'-aminopyrimidine ring of TDP; however, this step would occur only after an initial deprotonation of its own 4'-amino group. The mechanism of the initial deprotonation has been hypothesized, by analogy to transketolases, to occur via a histidine or an active site water molecule. Results from hybrid quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) reaction path calculations reveal an ∼10 kcal/mol difference in transition state energies, favoring a water mediated mechanism over direct deprotonation by histidine. This difference was determined to be largely governed by electrostatic changes induced by conformational variations in the active site. Additionally, mutagenesis studies reveal DXS to be an evolutionarily resilient enzyme. Particularly, we hypothesize that residues H82 and H304 may act in a compensatory fashion if the other is lost due to mutation. Further, nucleus-independent chemical shifts (NICSs) and aromatic stabilization energy (ASE) calculations suggest that reduction in TDP aromaticity also serves as a factor for regulating ylide formation and controlling reactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
X-ray crystallography-based structural elucidation of enzyme-bound intermediates along the 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase reaction coordinate.J Biol Chem. 2019 Aug 16;294(33):12405-12414. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009321. Epub 2019 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31239351 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback inhibition of deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase regulates the methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 7;288(23):16926-16936. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.464636. Epub 2013 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23612965 Free PMC article.
-
1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase, the gene product of open reading frame (ORF) 2816 and ORF 2895 in Rhodobacter capsulatus.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jan;183(1):1-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.1.1-11.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11114895 Free PMC article.
-
Thiamin (vitamin B1) biosynthesis and regulation: a rich source of antimicrobial drug targets?Int J Biol Sci. 2011 Jan 9;7(1):41-52. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7.41. Int J Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21234302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genes and enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of thiamin and thiamin diphosphate in yeasts.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2008;13(2):271-82. doi: 10.2478/s11658-007-0055-5. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18161008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of novel drug-like antitubercular hits targeting the MEP pathway enzyme DXPS by strategic application of ligand-based virtual screening.Chem Sci. 2022 Aug 8;13(36):10686-10698. doi: 10.1039/d2sc02371g. eCollection 2022 Sep 21. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 36320685 Free PMC article.
-
How the Destabilization of a Reaction Intermediate Affects Enzymatic Efficiency: The Case of Human Transketolase.ACS Catal. 2020 Feb 21;10(4):2872-2881. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b04690. Epub 2020 Feb 7. ACS Catal. 2020. PMID: 33828899 Free PMC article.
-
Trihydroxybenzaldoximes are Redox Cycling Inhibitors of ThDP-Dependent DXP Synthase.ACS Chem Biol. 2025 Jun 20;20(6):1195-1211. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5c00025. Epub 2025 May 18. ACS Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40383931
-
X-ray crystallography-based structural elucidation of enzyme-bound intermediates along the 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase reaction coordinate.J Biol Chem. 2019 Aug 16;294(33):12405-12414. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009321. Epub 2019 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31239351 Free PMC article.
-
A Theoretical Study of the Benzoylformate Decarboxylase Reaction Mechanism.Front Chem. 2018 Jun 26;6:205. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00205. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2018. PMID: 29998094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sacchettini JC, Poulter CD. Biochemistry: Creating Isoprenoid Diversity. Science. 1997;277:1788–1789. - PubMed
-
- Kuzuyama T, Seto H. Diversity of the Biosynthesis of the Isoprene Units. Nat Prod Rep. 2003;20:171–183. - PubMed
-
- Rohmer M. The Mevalonate-Independent Methylerythritol 4-Phosphate (MEP) Pathway for Isoprenoid Biosynthesis, Including Carotenoids. Pure Appl Chem. 1999;71:2279–2284.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

