Bronchoarterial ratio in never-smokers adults: Implications for bronchial dilation definition
- PMID: 27538197
- PMCID: PMC5161710
- DOI: 10.1111/resp.12875
Bronchoarterial ratio in never-smokers adults: Implications for bronchial dilation definition
Abstract
Background and objective: Bronchiectasis manifests as recurrent respiratory infections and reduced lung function. Airway dilation, which is measured as the ratio of the diameters of the bronchial lumen (B) and adjacent pulmonary artery (A), is a defining radiological feature of bronchiectasis. A challenge to equating the bronchoarterial (BA) ratio to disease severity is that the diameters of airway and vessel in health are not established. We sought to explore the variability of BA ratio in never-smokers without pulmonary disease and its associations with lung function.
Methods: Objective measurements of the BA ratio on volumetric computed tomography (CT) scans and pulmonary function data were collected in 106 never-smokers. The BA ratio was measured in the right upper lobe apical bronchus (RB1) and the right lower lobe basal posterior bronchus. The association between the BA ratio and forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1 ) was assessed using regression analysis.
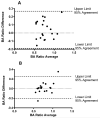
Results: The BA ratio was 0.79 ± 0.16 and was smaller in more peripheral RB1 bronchi (P < 0.0001). The BA ratio was >1, a typical threshold for bronchiectasis, in 10 (8.5%) subjects. Subjects with a BA ratio >1 versus ≤1 had smaller artery diameters (P < 0.0001) but not significantly larger bronchial lumens. After adjusting for age, gender, race and height, the BA ratio was directly related to FEV1 (P = 0.0007).
Conclusion: In never-smokers, the BA ratio varies by airway generation and is associated with lung function. A BA ratio >1 is driven by small arteries. Using artery diameter as reference to define bronchial dilation seems inappropriate.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00608764.
Keywords: bronchiectasis; bronchoarterial ratio; non-smoking; normal; volumetric computed tomography.
© 2016 Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Figures

References
-
- Amalakuhan B, Maselli DJ, Martinez-Garcia MA. Update in Bronchiectasis 2014. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192:1155–1161. - PubMed
-
- Parr DG, Guest PG, Reynolds JH, Dowson LJ, Stockley RA. Prevalence and impact of bronchiectasis in alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:1215–1221. - PubMed
-
- Park CS, Muller NL, Worthy SA, Kim JS, Awadh N, Fitzgerald M. Airway obstruction in asthmatic and healthy individuals: inspiratory and expiratory thin-section CT findings. Radiology. 1997;203:361–367. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

