Aspergillus nodules; another presentation of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- PMID: 27538521
- PMCID: PMC4991006
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-016-0276-3
Aspergillus nodules; another presentation of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
Abstract
Background: There are a number of different manifestations of pulmonary aspergillosis. This study aims to review the radiology, presentation, and histological features of lung nodules caused by Aspergillus spp.
Methods: Patients were identified from a cohort attending our specialist Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis clinic. Patients with cavitating lung lesions, with or without fibrosis and those with aspergillomas or a diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis were excluded. Demographic, laboratory, and clinical data and radiologic findings were recorded.
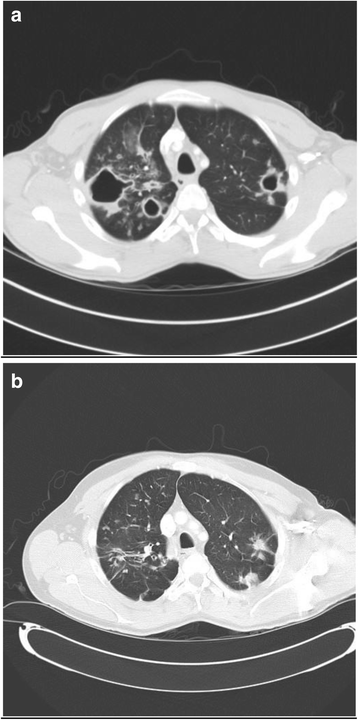
Results: Thirty-three patients with pulmonary nodules and diagnostic features of aspergillosis (histology and/or laboratory findings) were identified. Eighteen (54.5 %) were male, mean age 58 years (range 27-80 years). 19 (57.6 %) were former or current smokers. The median Charleston co-morbidity index was 3 (range 0-7). All complained of a least one of; dyspnoea, cough, haemoptysis, or weight loss. None reported fever. Ten patients (31 %) did not have an elevated Aspergillus IgG, and only 4 patients had elevated Aspergillus precipitins. Twelve patients (36 %) had a single nodule, six patients (18 %) had between 2 and 5 nodules, 2 (6 %) between 6 and 10 nodules and 13 (39 %) had more than 10 nodules. The mean size of the nodules was 21 mm, with a maximum size ranging between 5-50 mm. No nodules had cavitation radiographically. The upper lobes were most commonly involved. Histology was available for 18 patients and showed evidence of granulation tissue, fibrosis, and visualisation of fungal hyphae.
Conclusion: Pulmonary nodules are a less common manifestation of aspergillosis in immunocompetent patients. Distinguishing these nodules from other lung pathology may be difficult on CT findings alone.
Keywords: Aspergillus; Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis; Fungal infection of lung; Pulmonary nodule.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompetent patients without air-meniscus sign and underlying lung disease: CT findings and histopathologic features.Acta Radiol. 2011 Sep 1;52(7):756-61. doi: 10.1258/ar.2011.100481. Epub 2011 May 19. Acta Radiol. 2011. PMID: 21596796
-
Aspergilloma.2024 Jan 31. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jan 31. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31536274 Free Books & Documents.
-
Expanding the spectrum of chronic necrotising (semi-invasive) aspergillosis: a series of eight cases presenting as radiologically solid lung nodules mimicking malignancy.Histopathology. 2020 Apr;76(5):685-697. doi: 10.1111/his.14037. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Histopathology. 2020. PMID: 31743469
-
Chronic Aspergillosis of the Lungs: Unravelling the Terminology and Radiology.Eur Radiol. 2015 Oct;25(10):3100-7. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3690-7. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Eur Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25791639 Review.
-
Manifestations of pulmonary aspergillosis in pediatrics.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020 Jun;32(3):389-394. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000898. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32371841 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical manifestations, associated risk factors and treatment outcomes of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA): Experiences from a tertiary care hospital in Lahore, Pakistan.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 12;16(11):e0259766. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259766. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34767589 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical spectrum of aspergillosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Infection. 2023 Aug;51(4):813-829. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01960-2. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Infection. 2023. PMID: 36662439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Weight loss and diabetes are new risk factors for the development of invasive aspergillosis infection in non-immunocompromized humans.Clin Pract (Lond). 2017;14(5 Spec Iss):296-301. doi: 10.4172/clinical-practice.1000125. Clin Pract (Lond). 2017. PMID: 29670744 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Pulmonary Diseases Associated with Aspergillosis: Is There a Connection?Mycopathologia. 2017 Dec;182(11-12):1125-1129. doi: 10.1007/s11046-017-0176-y. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Mycopathologia. 2017. PMID: 28702854
-
Chronic Pulmonary Histoplasmosis-A Scoping Literature Review.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Apr 6;7(5):ofaa119. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa119. eCollection 2020 May. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32411810 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

