Curcumin suppresses NTHi-induced CXCL5 expression via inhibition of positive IKKβ pathway and up-regulation of negative MKP-1 pathway
- PMID: 27538525
- PMCID: PMC4990917
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31695
Curcumin suppresses NTHi-induced CXCL5 expression via inhibition of positive IKKβ pathway and up-regulation of negative MKP-1 pathway
Abstract
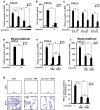
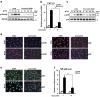
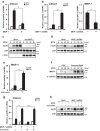
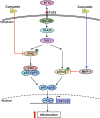
Otitis media (OM) is the most common childhood bacterial infection, and leading cause of conductive hearing loss. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) is a major bacterial pathogen for OM. OM characterized by the presence of overactive inflammatory responses is due to the aberrant production of inflammatory mediators including C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 5 (CXCL5). The molecular mechanism underlying induction of CXCL5 by NTHi is unknown. Here we show that NTHi up-regulates CXCL5 expression by activating IKKβ-IκBα and p38 MAPK pathways via NF-κB nuclear translocation-dependent and -independent mechanism in middle ear epithelial cells. Current therapies for OM are ineffective due to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant NTHi strains and risk of side effects with prolonged use of immunosuppressant drugs. In this study, we show that curcumin, derived from Curcuma longa plant, long known for its medicinal properties, inhibited NTHi-induced CXCL5 expression in vitro and in vivo. Curcumin suppressed CXCL5 expression by direct inhibition of IKKβ phosphorylation, and inhibition of p38 MAPK via induction of negative regulator MKP-1. Thus, identification of curcumin as a potential therapeutic for treating OM is of particular translational significance due to the attractiveness of targeting overactive inflammation without significant adverse effects.
Figures
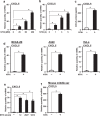
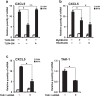
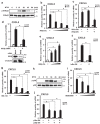
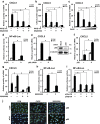
Similar articles
-
Activation of NF-kappa B by nontypeable Hemophilus influenzae is mediated by toll-like receptor 2-TAK1-dependent NIK-IKK alpha /beta-I kappa B alpha and MKK3/6-p38 MAP kinase signaling pathways in epithelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jul 17;98(15):8774-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.151236098. Epub 2001 Jul 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11438700 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin inhibits NTHi-triggered CXCR4 activation through suppressing IKKα/NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in otitis media.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jul;42(1):248-258. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3577. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29568908 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of interleukin-8 by novel small cytoplasmic molecules of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae via p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways.Infect Immun. 2003 Oct;71(10):5523-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.10.5523-5530.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 14500470 Free PMC article.
-
Exploitation of host epithelial signaling networks by respiratory bacterial pathogens.J Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Jan;91(1):1-7. doi: 10.1254/jphs.91.1. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12686724 Review.
-
[Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) epidemiology].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2011 May;85(3):227-37. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi.85.227. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2011. PMID: 21706841 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Role of Oxidative Stress in Cochlear Hair Cell Death: Prospective Phytochemical Therapeutics against Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 12;25(8):4272. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084272. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Panel 8: Vaccines and immunology.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Mar;130 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):109839. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109839. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31948716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of NTHi colonization and infection in the pathogenesis of neutrophilic asthma.Respir Res. 2020 Jul 3;21(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01438-5. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32620122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin Inhibits NTHi-Induced MUC5AC Mucin Overproduction in Otitis Media via Upregulation of MAPK Phosphatase MKP-1.Int J Inflam. 2017;2017:4525309. doi: 10.1155/2017/4525309. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Int J Inflam. 2017. PMID: 28487811 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Evaluation of the Antimicrobial-Immunomodulatory Dual Action of Xenohormetic Molecules against Haemophilus influenzae Respiratory Infection.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 17;9(12):891. doi: 10.3390/biom9120891. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31861238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giebink G. S. Immunoprophylaxis of otitis media. Adv Exp Med Biol 303, 149–158 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Arguedas A., Kvaerner K., Liese J., Schilder A. G. & Pelton S. I. Otitis media across nine countries: disease burden and management. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74, 1419–1424 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Ito M. et al.. Clonal spread of beta-lactamase-producing amoxicillin-clavulanate-resistant (BLPACR) strains of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae among young children attending a day care in Japan. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74, 901–906 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

