A comparison between quantitative PCR and droplet digital PCR technologies for circulating microRNA quantification in human lung cancer
- PMID: 27538962
- PMCID: PMC4991011
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-016-0292-7
A comparison between quantitative PCR and droplet digital PCR technologies for circulating microRNA quantification in human lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Selected microRNAs (miRNAs) that are abnormally expressed in the serum of patients with lung cancer have recently been proposed as biomarkers of this disease. The measurement of circulating miRNAs, however, requires a highly reliable quantification method. Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) is the most commonly used method, but it lacks reliable endogenous reference miRNAs for normalization of results in biofluids. When used in absolute quantification, it must rely on the use of external calibrators. Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) is a recently introduced technology that overcomes the normalization issue and may facilitate miRNA measurement. Here we compared the performance of absolute qPCR and ddPCR techniques for quantifying selected miRNAs in the serum.
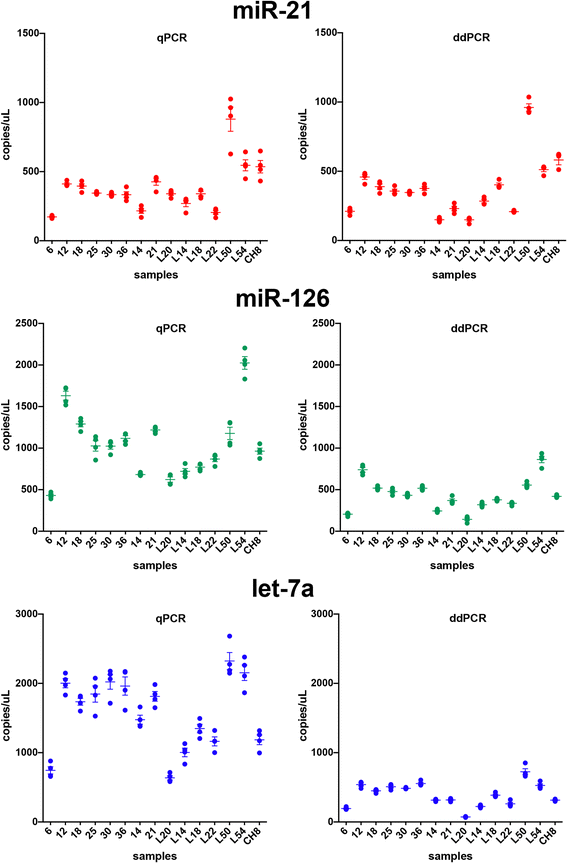
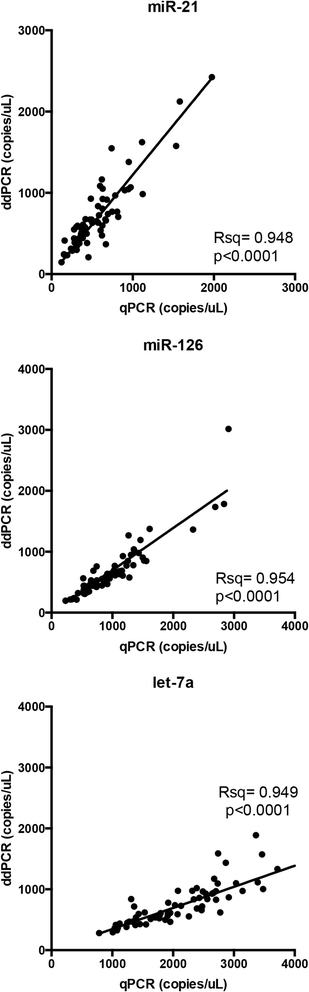
Results: In the first experiment, three miRNAs, proposed in the literature as lung cancer biomarkers (miR-21, miR-126 and let-7a), were analyzed in a set of 15 human serum samples. Four independent qPCR and four independent ddPCR amplifications were done on the same samples and used to estimate the precision and correlation of miRNA measurements obtained with the two techniques. The precision of the two methods was evaluated by calculating the Coefficient of Variation (CV) of the four independent measurements obtained with each technique. The CV was similar or smaller in ddPCR than in qPCR for all miRNAs tested, and was significantly smaller for let-7a (p = 0.028). Linear regression analysis of the miRNA values obtained with qPCR and ddPCR showed strong correlation (p < 0.001). To validate the correlation obtained with the two techniques in the first experiment, in a second experiment the same miRNAs were measured in a larger cohort (70 human serum samples) by both qPCR and ddPCR. The correlation of miRNA analyses with the two methods was significant for all three miRNAs. Moreover, in our experiments the ddPCR technique had higher throughput than qPCR, at a similar cost-per-sample.
Conclusions: Analyses of serum miRNAs performed with qPCR and ddPCR were largely concordant. Both qPCR and ddPCR can reliably be used to quantify circulating miRNAs, however, ddPCR revealed similar or greater precision and higher throughput of analysis.
Keywords: Droplet digital PCR; Lung cancer; Serum biomarkers; microRNAs; qPCR.
Figures


References
-
- Jaklitsch MT, Jacobson FL, Austin JH, Field JK, Jett JR, Keshavjee S, MacMahon H, Mulshine JL, Munden RF, Salgia R, et al. The American Association for Thoracic Surgery guidelines for lung cancer screening using low-dose computed tomography scans for lung cancer survivors and other high-risk groups. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;144(1):33–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.05.060. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dominioni L, Poli A, Mantovani W, Pisani S, Rotolo N, Paolucci M, Sessa F, Conti V, D’Ambrosio V, Paddeu A, et al. Assessment of lung cancer mortality reduction after chest X-ray screening in smokers: a population-based cohort study in Varese, Italy. Lung Cancer. 2013;80(1):50–4. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.12.014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

