Towards malaria elimination in the MOSASWA (Mozambique, South Africa and Swaziland) region
- PMID: 27538990
- PMCID: PMC4991067
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-016-1470-8
Towards malaria elimination in the MOSASWA (Mozambique, South Africa and Swaziland) region
Abstract
The substantial impact of cross-border collaborative control efforts on the burden of malaria in southern Africa has previously been demonstrated through the successes of the Lubombo Spatial Development Initiative. Increases in malaria cases recorded in the three partner countries (Mozambique, South Africa, Swaziland) since termination of that programme in 2011 have provided impetus for the resuscitation of cooperation in the form of the MOSASWA malaria initiative. MOSASWA, launched in 2015, seeks to renew regional efforts to accelerate progress towards malaria elimination goals already established in the region. National malaria programmes, together with developmental partners, academic institutions and the private sector seek to harmonize policy, strengthen capacity, share expertise, expand access to elimination interventions particularly amongst migrant and border population groups, mobilize resources and advocate for long-term funding to ultimately achieve and sustain malaria elimination in the MOSASWA region.
Keywords: Cross-border; Elimination; Malaria; Southern Africa.
Figures
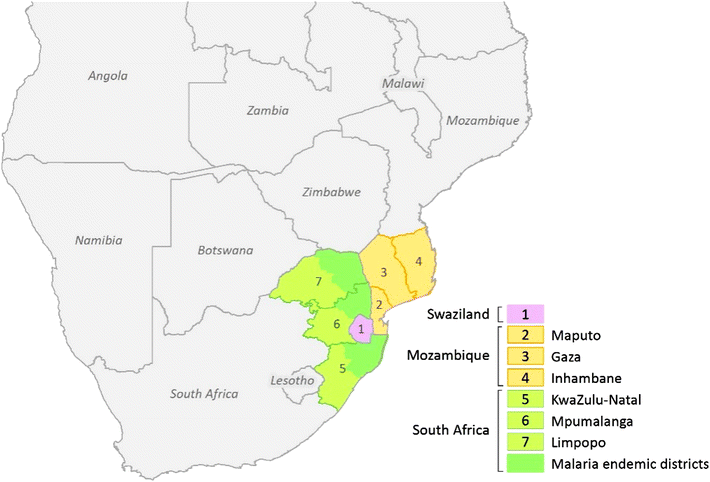
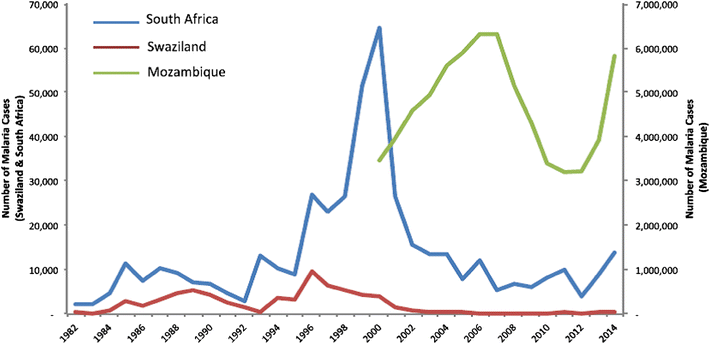
References
-
- WHO. Global technical strategy (GTS) 2016–30. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015.
-
- Roll Back Malaria. Action and investment (AIM) strategy 2016–30. Geneva; 2015.
-
- South African National Department of Health. Malaria elimination strategy 2012–2018. Pretoria; 2012.
-
- Swaziland Ministry of Health and Social Welfare. Malaria elimination strategy 2008–2015. Mbabane; 2008.
-
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

