Global electrical heterogeneity: A review of the spatial ventricular gradient
- PMID: 27539162
- PMCID: PMC5159246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2016.07.025
Global electrical heterogeneity: A review of the spatial ventricular gradient
Abstract
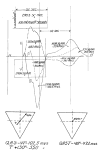
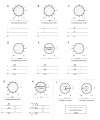
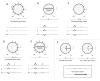
The ventricular gradient, an electrocardiographic concept calculated by integrating the area under the QRS complex and T-wave, represents the degree and direction of myocardial electrical heterogeneity. Although the concept of the ventricular gradient was first introduced in the 1930s, it has not yet found a place in routine electrocardiography. In the modern era, it is relatively simple to calculate the ventricular gradient in three dimensions (the spatial ventricular gradient (SVG)), and there is now renewed interest in using the SVG as a tool for risk stratification of ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. This manuscript will review the history of the ventricular gradient, describe its electrophysiological meaning and significance, and discuss its clinical utility.
Keywords: Spatial ventricular gradient; Vectorcardiogram.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Wilson FN, Macleod AG, Barker PS, Johnston FD. The determination and the significance of the areas of the ventricular deflections of the electrocardiogram. American Heart Journal. 1934;10:46–61.
-
- Wilson FN, Macleon FS, Barker PS. The T Deflection of the Electrocardiogram. Transactions of the Association of American Physicians. 1931;46:29–38.
-
- Ashman R, Byer E. The normal human ventricular gradient: I. Factors which affect its direction and its relation to the mean QRS axis. American Heart Journal. 1943;25:16–35.
-
- Gardberg M, Rosen IL. Monophasic curve analysis and the ventricular gradient in the electrogram of strips of turtle ventricle. Circ Res. 1959;7:870–5. - PubMed
-
- Burch GE, Abildskov AA, Cronvich JA. A study of the spatial vectorcardiogram of the ventricular gradient. Circulation. 1954;9:267–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

