Genome-wide association study identifies 14 novel risk alleles associated with basal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27539887
- PMCID: PMC4992160
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12510
Genome-wide association study identifies 14 novel risk alleles associated with basal cell carcinoma
Abstract
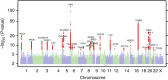
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer worldwide with an annual incidence of 2.8 million cases in the United States alone. Previous studies have demonstrated an association between 21 distinct genetic loci and BCC risk. Here, we report the results of a two-stage genome-wide association study of BCC, totalling 17,187 cases and 287,054 controls. We confirm 17 previously reported loci and identify 14 new susceptibility loci reaching genome-wide significance (P<5 × 10(-8), logistic regression). These newly associated SNPs lie within predicted keratinocyte regulatory elements and in expression quantitative trait loci; furthermore, we identify candidate genes and non-coding RNAs involved in telomere maintenance, immune regulation and tumour progression, providing deeper insight into the pathogenesis of BCC.
Conflict of interest statement
David Hinds is an employee at 23andMe. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined analysis of keratinocyte cancers identifies novel genome-wide loci.Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Sep 15;28(18):3148-3160. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz121. Hum Mol Genet. 2019. PMID: 31174203 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and functional interaction network analysis reveals global enrichment of regulatory T cell genes influencing basal cell carcinoma susceptibility.Genome Med. 2021 Feb 6;13(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00827-9. Genome Med. 2021. PMID: 33549134 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study identifies novel alleles associated with risk of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Sep 15;20(18):3718-24. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr287. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21700618 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association studies and polygenic risk scores for skin cancer: clinically useful yet?Br J Dermatol. 2019 Dec;181(6):1146-1155. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17917. Epub 2019 Jul 7. Br J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30908599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UV-Induced Molecular Signaling Differences in Melanoma and Non-melanoma Skin Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:27-40. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-56017-5_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29124688 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer PRSweb: An Online Repository with Polygenic Risk Scores for Major Cancer Traits and Their Evaluation in Two Independent Biobanks.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Nov 5;107(5):815-836. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.08.025. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 32991828 Free PMC article.
-
Common genetic polymorphisms contribute to the association between chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-melanoma skin cancer.Int J Epidemiol. 2021 Aug 30;50(4):1325-1334. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyab042. Int J Epidemiol. 2021. PMID: 33748835 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic Risk and Chemotherapy-Related Subsequent Malignancies in Childhood Cancer Survivors: A Childhood Cancer Survivor Study and St Jude Lifetime Cohort Study Report.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep 20;41(27):4381-4393. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00428. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37459583 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring various polygenic risk scores for skin cancer in the phenomes of the Michigan genomics initiative and the UK Biobank with a visual catalog: PRSWeb.PLoS Genet. 2019 Jun 13;15(6):e1008202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008202. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31194742 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors and Innovations in Risk Assessment for Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, and Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 29;16(5):1016. doi: 10.3390/cancers16051016. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473375 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kauvar A. N. B. et al. Consensus for nonmelanoma skin cancer treatment: basal cell carcinoma, including a cost analysis of treatment methods. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. Al. 41, 550–571 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Stacey S. N. et al. Common variants on 1p36 and 1q42 are associated with cutaneous basal cell carcinoma but not with melanoma or pigmentation traits. Nat. Genet. 40, 1313–1318 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

