Orexin-A/Hypocretin-1 Mediates Cocaine-Seeking Behavior in the Posterior Paraventricular Nucleus of the Thalamus via Orexin/Hypocretin Receptor-2
- PMID: 27540003
- PMCID: PMC5074483
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.116.235945
Orexin-A/Hypocretin-1 Mediates Cocaine-Seeking Behavior in the Posterior Paraventricular Nucleus of the Thalamus via Orexin/Hypocretin Receptor-2
Abstract
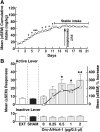
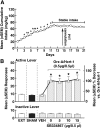
Orexin/hypocretin (Orx/Hcrt) projections from the lateral hypothalamus to the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus (PVT) are implicated in drug addiction. Specifically, the posterior section of the PVT (pPVT) innervates brain structures that modulate motivated behavior. This study investigated the role of pPVT-Orx/Hcrt transmission in cocaine-seeking behavior. Because the effects of Orx/Hcrt are mediated by two Orx/Hcrt receptors (Hcrt-r1 and Hcrt-r2), we examined the extent to which Hcrt-r1 and Hcrt-r2 are involved in Orx/Hcrt-induced cocaine seeking. Male Wistar rats were made cocaine dependent by self-administering cocaine 6 hours/day (long access) for 21 days. After self-administration training, the rats underwent daily extinction training, during which cocaine was withheld. After extinction, the rats were injected into the pPVT with Orx-A/Hcrt-1 (0-2 µg) alone or, using a single dose of 0.5 µg, in combination with an Hcrt-r1 antagonist (SB334867; 0-15 µg) or an Hcrt-r2 antagonist (TCSOX229; 0-15 µg). Orx-A/Hcrt-1 alone reinstated (primed) cocaine seeking. Unexpectedly, coadministration of Orx-A/Hcrt-1 with SB334867 did not have any effects on Orx-A/Hcrt-1-induced reinstatement, whereas when coadministered with Orx-A/Hcrt-1, TCSOX229 prevented cocaine-seeking behavior. These results indicate that Hcrt-r2 in the pPVT mediates the reinstating effect of Orx-A/Hcrt-1 in animals with a history of cocaine dependence and further identify Hcrt-r2 as a possible molecular target that can guide future therapeutic approaches for the prevention of drug-seeking behavior.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blockade of hypocretin receptor-1 preferentially prevents cocaine seeking: comparison with natural reward seeking.Neuroreport. 2014 May 7;25(7):485-8. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000120. Neuroreport. 2014. PMID: 24407199 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Hypocretin-1/Orexin-A Neurons Projecting to the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis and Paraventricular Nucleus Is Critical for Reinstatement of Alcohol Seeking by Neuropeptide S.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Mar 15;79(6):452-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.04.021. Epub 2015 May 2. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26055195
-
Dynorphin Counteracts Orexin in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Thalamus: Cellular and Behavioral Evidence.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Apr;43(5):1010-1020. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.250. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29052613 Free PMC article.
-
The paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus is recruited by both natural rewards and drugs of abuse: recent evidence of a pivotal role for orexin/hypocretin signaling in this thalamic nucleus in drug-seeking behavior.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 Apr 3;8:117. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00117. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24765071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cocaine abuse and midbrain circuits: Functional anatomy of hypocretin/orexin transmission and therapeutic prospect.Brain Res. 2020 Mar 15;1731:146164. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.02.026. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 30796894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cocaine-Seeking Behavior Induced by Orexin A Administration in the Posterior Paraventricular Nucleus of the Thalamus Is Not Long-Lasting: Neuroadaptation of the Orexin System During Cocaine Abstinence.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Feb 23;15:620868. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.620868. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33708078 Free PMC article.
-
phMRI, neurochemical and behavioral responses to psychostimulants distinguishing genetically selected alcohol-preferring from genetically heterogenous rats.Addict Biol. 2019 Sep;24(5):981-993. doi: 10.1111/adb.12671. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Addict Biol. 2019. PMID: 30328656 Free PMC article.
-
The Orexin/Receptor System: Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential for Neurological Diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jun 28;11:220. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00220. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30002617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of a cortico-thalamic circuit attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in "relapse prone" male rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Apr;239(4):1035-1051. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05894-9. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 34181035
-
Orexin/Hypocretin System: Role in Food and Drug Overconsumption.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017;136:199-237. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 29056152 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed SH, Kenny PJ, Koob GF, Markou A. (2002) Neurobiological evidence for hedonic allostasis associated with escalating cocaine use. Nat Neurosci 5:625–626. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF. (1998) Transition from moderate to excessive drug intake: change in hedonic set point. Science 282:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF. (1999) Long-lasting increase in the set point for cocaine self-administration after escalation in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 146:303–312. - PubMed
-
- Azizi H, Mirnajafi-Zadeh J, Rohampour K, Semnanian S. (2010) Antagonism of orexin type 1 receptors in the locus coeruleus attenuates signs of naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal in rats. Neurosci Lett 482:255–259. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

