Possible Mechanisms for Functional Antagonistic Effect of Ferula assafoetida on Muscarinic Receptors in Tracheal Smooth Muscle
- PMID: 27540324
- PMCID: PMC4975587
Possible Mechanisms for Functional Antagonistic Effect of Ferula assafoetida on Muscarinic Receptors in Tracheal Smooth Muscle
Abstract
Background: The contribution of histamine (H1) receptors inhibitory and/or β-adrenoceptors stimulatory mechanisms in the relaxant property of Ferula assa-foetida. (F. asafoetida) was examined in the present study.
Methods: We evaluated the effect of three concentrations of F. asafoetida extract (2.5, 5, and 10 mg/mL), a muscarinic receptors antagonist, and saline on methacholine concentration-response curve in tracheal smooth muscles incubated with β-adrenergic and histamine (H1) (group 1), and only β-adrenergic (group 2) receptors antagonists.
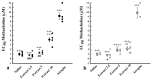
Results: EC50 values in the presence of atropine, extract (5 and 10 mg/mL) and maximum responses to methacholine due to the 10 mg/mL extract in both groups and 5 mg/mL extract in group 1 were higher than saline (P < 0.0001, P = 0.0477, and P = 0.0008 in group 1 and P < 0.0001, P = 0.0438, and P = 0.0107 in group 2 for atropine, 5 and 10 mg/mL extract, respectively). Values of concentration ratio minus one (CR-1), in the presence of extracts were lower than atropine in both groups (P = 0.0339 for high extract concentration in group 1 and P < 0.0001 for other extract concentrations in both groups).
Conclusion: Histamine (H1) receptor blockade affects muscarinic receptors inhibitory property of F. asafoetida in tracheal smooth muscle.
Keywords: Ferula extract; muscarinic receptors; muscle relaxation.
Figures


References
-
- Takeoka G. Volatile Constituents of Asafoetida, Aroma Active Compounds in Foods. Am Chemic Soc. 2001;794:33–44. doi: 10.1021/bk-2001-0794.ch004. - DOI
-
- Evans WC. Trease and Evans Pharmacognosy. London (LDN): WB Saunders; 2002. p. 286. - DOI
-
- Zargari A. Medicinal Plants. Sixth ed. Tehran (TEH): Tehran University Tehran Publications; 1996.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
