Olfactory Receptors Modulate Physiological Processes in Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells
- PMID: 27540365
- PMCID: PMC4972829
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00339
Olfactory Receptors Modulate Physiological Processes in Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
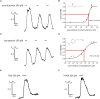
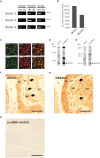
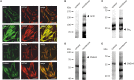
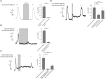
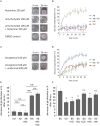
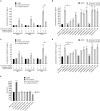
Pathophysiological mechanisms in human airway smooth muscle cells (HASMCs) significantly contribute to the progression of chronic inflammatory airway diseases with limited therapeutic options, such as severe asthma and COPD. These abnormalities include the contractility and hyperproduction of inflammatory proteins. To develop therapeutic strategies, key pathological mechanisms, and putative clinical targets need to be identified. In the present study, we demonstrated that the human olfactory receptors (ORs) OR1D2 and OR2AG1 are expressed at the RNA and protein levels in HASMCs. Using fluorometric calcium imaging, specific agonists for OR2AG1 and OR1D2 were identified to trigger transient Ca(2+) increases in HASMCs via a cAMP-dependent signal transduction cascade. Furthermore, the activation of OR2AG1 via amyl butyrate inhibited the histamine-induced contraction of HASMCs, whereas the stimulation of OR1D2 with bourgeonal led to an increase in cell contractility. In addition, OR1D2 activation induced the secretion of IL-8 and GM-CSF. Both effects were inhibited by the specific OR1D2 antagonist undecanal. We herein provide the first evidence to show that ORs are functionally expressed in HASMCs and regulate pathophysiological processes. Therefore, ORs might be new therapeutic targets for these diseases, and blocking ORs could be an auspicious strategy for the treatment of early-stage chronic inflammatory lung diseases.
Keywords: contraction; cytokines; olfactory receptor; signaling; smooth muscle cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TNFα-induced airway smooth muscle cell proliferation depends on endothelin receptor signaling, GM-CSF and IL-6.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:188-99. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.07.008. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27422754
-
Human olfactory sensitivity for bourgeonal and male infertility: a preliminary investigation.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Nov;270(12):3079-86. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2441-0. Epub 2013 Mar 24. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23525651
-
TNFalpha-induced GM-CSF release from human airway smooth muscle cells depends on activation of an ET-1 autoregulatory positive feedback mechanism.Thorax. 2009 Dec;64(12):1044-52. doi: 10.1136/thx.2008.111047. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Thorax. 2009. PMID: 19850966
-
Mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of hyper-contractility of bronchial smooth muscle in allergic asthma.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2017;53(0):37-47. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.53.37. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2017. PMID: 28484126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Airway smooth muscle as a target of glucocorticoid action in the treatment of asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Nov;158(5 Pt 3):S201-6. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.supplement_2.13tac190. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. PMID: 9817746 Review.
Cited by
-
Ectopic Odorant Receptor Responding to Flavor Compounds: Versatile Roles in Health and Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 23;13(8):1314. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081314. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduction of Asthmatic Parameters by Sea Hare Hydrolysates in a Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma.Nutrients. 2017 Jul 5;9(7):699. doi: 10.3390/nu9070699. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28678189 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory receptor 10J5 responding to α-cedrene regulates hepatic steatosis via the cAMP-PKA pathway.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 25;7(1):9471. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10379-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28842679 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory receptors in neural regeneration in the central nervous system.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Sep 1;20(9):2480-2494. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00495. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39503417 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory, Taste, and Photo Sensory Receptors in Non-sensory Organs: It Just Makes Sense.Front Physiol. 2018 Nov 27;9:1673. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01673. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30542293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artamonov M. V., Momotani K., Stevenson A., Trentham D. R., Derewenda U., Derewenda Z. S., et al. . (2013). Agonist-induced Ca2+ sensitization in smooth muscle: redundancy of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors (RhoGEFs) and response kinetics, a caged compound study. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 34030–34040. 10.1074/jbc.M113.514596 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

