Development of a qPCR Strategy to Select Bean Genes Involved in Plant Defense Response and Regulated by the Trichoderma velutinum - Rhizoctonia solani Interaction
- PMID: 27540382
- PMCID: PMC4973505
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01109
Development of a qPCR Strategy to Select Bean Genes Involved in Plant Defense Response and Regulated by the Trichoderma velutinum - Rhizoctonia solani Interaction
Abstract
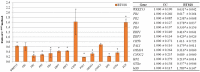
Bean production is affected by a wide diversity of fungal pathogens, among them Rhizoctonia solani is one of the most important. A strategy to control bean infectious diseases, mainly those caused by fungi, is based on the use of biocontrol agents (BCAs) that can reduce the negative effects of plant pathogens and also can promote positive responses in the plant. Trichoderma is a fungal genus that is able to induce the expression of genes involved in plant defense response and also to promote plant growth, root development and nutrient uptake. In this article, a strategy that combines in silico analysis and real time PCR to detect additional bean defense-related genes, regulated by the presence of Trichoderma velutinum and/or R. solani has been applied. Based in this strategy, from the 48 bean genes initially analyzed, 14 were selected, and only WRKY33, CH5b and hGS showed an up-regulatory response in the presence of T. velutinum. The other genes were or not affected (OSM34) or down-regulated by the presence of this fungus. R. solani infection resulted in a down-regulation of most of the genes analyzed, except PR1, OSM34 and CNGC2 that were not affected, and the presence of both, T. velutinum and R. solani, up-regulates hGS and down-regulates all the other genes analyzed, except CH5b which was not significantly affected. As conclusion, the strategy described in the present work has been shown to be effective to detect genes involved in plant defense, which respond to the presence of a BCA or to a pathogen and also to the presence of both. The selected genes show significant homology with previously described plant defense genes and they are expressed in bean leaves of plants treated with T. velutinum and/or infected with R. solani.
Keywords: Phaseolus vulgaris; biocontrol agent; biotic stress; defense genes; hypersensitive response; induced systemic resistance; systemic acquired resistance.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of Trichoderma velutinum and Rhizoctonia solani on the Metabolome of Bean Plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 28;20(3):549. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030549. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30696057 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Rhizoctonia solani and Trichoderma spp. in growth of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and in the induction of plant defense-related genes.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Sep 16;6:685. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00685. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26442006 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of defense-related genes in mung bean varieties in response to Trichoderma virens alone and in the presence of Rhizoctonia solani infection.3 Biotech. 2018 Oct;8(10):432. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1453-2. Epub 2018 Sep 29. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30306001 Free PMC article.
-
Trichoderma spp. Genes Involved in the Biocontrol Activity Against Rhizoctonia solani.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 25;13:884469. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.884469. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35694310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antagonist effects of strains of Bacillus spp. against Rhizoctonia solani for their protection against several plant diseases: Alternatives to chemical pesticides.C R Biol. 2019 Jun-Aug;342(5-6):124-135. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 Aug 9. C R Biol. 2019. PMID: 31402177 Review.
Cited by
-
Spores of Trichoderma Strains over P. vulgaris Beans: Direct Effect on Insect Attacks and Indirect Effect on Agronomic Parameters.Insects. 2022 Nov 25;13(12):1086. doi: 10.3390/insects13121086. Insects. 2022. PMID: 36554996 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic characterization of Trichoderma harzianum T34 primed tomato plants: assessment of biocontrol agent induced host specific gene expression and plant growth promotion.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Nov 8;23(1):552. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04502-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37940862 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of Pathogen Resistance in Common Bean Plants by Inoculation With Rhizobium etli.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Oct 22;10:1317. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01317. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31695715 Free PMC article.
-
Trichoderma erinaceum Bio-Priming Modulates the WRKYs Defense Programming in Tomato Against the Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici (Fol) Challenged Condition.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jul 30;10:911. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00911. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31428107 Free PMC article.
-
Organic and Conventional Bean Pesticides in Development of Autochthonous Trichoderma Strains.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jun 3;8(6):603. doi: 10.3390/jof8060603. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barthelson R. A., Qaisar U., Galbraith D. W. (2010). Functional analysis of the Gossypium arboreum genome. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 28 334–343. 10.1007/s11105-009-0157-5 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

