The role of growth factors on hepatic damage in rats with obstructive jaundice
- PMID: 27540507
- PMCID: PMC4975730
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-016-2919-5
The role of growth factors on hepatic damage in rats with obstructive jaundice
Abstract
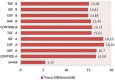
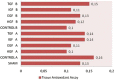
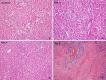
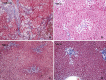
In this study, we investigated the affect and the role of growth factors on liver damage. 110 Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 11 groups: a sham group, a control group, HGF, EGF, IGF, TGF groups of irreversible jaundiced rats and a control group and HGF, EGF, IGF, and TGF groups of reversible jaundiced rats (n = 10). In the irreversible jaundiced groups, the common bile duct was explorated, double ligated, and cut. 150 μg/kg/day HGF, 5 μg/kg/day EGF, 5 μg/kg/day IGF, and 5 μg/kg/day TGF β-1 were injected intraperitoneally after the seventh post-operative day. In the reversible jaundiced group, the common bile duct was ligated and the ligation was resolved on the seventh post-operative day. For 5 days, growth factors were injected at the same dose. Ductal proliferation scores significantly decreased after growth factor administration in the EGF-A and TGF-A groups. Furthermore, ductal proliferation was decreased in the TGF-B group. As a result of this study, HGF was effective in the irreversible jaundiced groups and ineffective in the reversible jaundice groups. EGF was effective in the reversible jaundiced groups and ineffective in the irreversible jaundiced groups. In both the irreversible jaundiced and reversible jaundiced groups, IGF was ineffective, although TGF β-1 was effective. We believe that these results arise from the positive effects of effective doses of growth factor on liver damage.
Keywords: Growth factors; Hepatic injury; Obstructive jaundice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delayed liver regeneration with negative regulation of hepatocyte growth factor and positive regulation of transforming growth factor-beta1 mRNA after portal branch ligation in biliary obstructed rats.Surgery. 2002 Feb;131(2):163-71. doi: 10.1067/msy.2002.119818. Surgery. 2002. PMID: 11854694
-
Single dose of anti-transforming growth factor-beta1 monoclonal antibody enhances liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in biliary-obstructed rats.J Surg Res. 2006 Dec;136(2):280-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2006.08.020. Epub 2006 Oct 13. J Surg Res. 2006. PMID: 17046790
-
Hepatocyte growth factor supply accelerates compensatory hypertrophy caused by portal branch ligation in normal and jaundiced rats.J Surg Res. 1999 Jul;85(1):115-9. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1999.5639. J Surg Res. 1999. PMID: 10383847
-
Beneficial effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I on intestinal bacterial translocation, endotoxemia, and apoptosis in experimentally jaundiced rats.J Am Coll Surg. 2000 Apr;190(4):423-31. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(99)00285-9. J Am Coll Surg. 2000. PMID: 10757380
-
Effect of 5-lipoxygenase inhibition on Kupffer cell clearance capacity in obstructive jaundiced rats.J Surg Res. 2001 Apr;96(2):158-62. doi: 10.1006/jsre.2000.6058. J Surg Res. 2001. PMID: 11266267
Cited by
-
The effect of Farnesoid X receptor agonist tropifexor on liver damage in rats with experimental obstructive jaundice.Acta Cir Bras. 2021 Oct 25;36(9):e360902. doi: 10.1590/ACB360902. eCollection 2021. Acta Cir Bras. 2021. PMID: 34818403 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the metabolic mechanism of scoparone on biomarkers for inhibiting Yanghuang syndrome.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 21;6:37519. doi: 10.1038/srep37519. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27869223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desbois-Mouthon C, Wendum D, Cadoret A, Rey C, Leneuve P, Blaise A, Housset C, Tronche F, Le Bouc Y, Holzenberger M. Hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration is impaired in mice with liver-specific IGF-1R knockout. FASEB J. 2006;20(6):773–775. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

