Thymoquinone Could Increase The Efficacy of Tamoxifen Induced Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 27540530
- PMCID: PMC4988424
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2016.4320
Thymoquinone Could Increase The Efficacy of Tamoxifen Induced Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
Objective: Thymoquinone (TQ), as the main component of Nigella Sativa plant, shows anticancer properties. This study was aimed to evaluate the combined effect of TQ and Tamoxifen (TAM) on viability and apoptosis of human breast cancer cell lines.
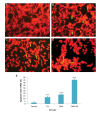
Materials and methods: In this experimental study, estrogen positive MCF-7 and estrogen negative MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell lines were induced by TAM (2 µM) or different doses of TQ (50, 75, 100, 150 µM), individually or in combination. Cell viability and apoptosis were investigated by MTT assay and TdT-mediated deoxy-uracil nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay; Acridine orange (AO)/Ethidium bromide (EB) staining respectively. Data were analyzed by one way ANOVA and P<0.05 was considered significant.
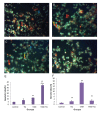
Results: In 24 hours treatment, TAM and all doses of TQ, solely or in combination, significantly reduced cell viability of both cell lines, except in MCF-7 cells treated with 50 µM TQ, and MDA-MB-231 cells treated with 50 or 75 µM TQ (P<0.01). After 48 hours treatment, cell viability of both cell lines was reduced in all treated groups (P<0.05). Remarkable apoptotic index was observed in combination treatment of MCF-7 or MDA-MB-231 cell lines with TAM and TQ (P<0.001).
Conclusion: The synergistic effect of TQ and TAM on human breast cancer cell lines showed cell viability reduction as well as apoptosis induction, independent to estrogen.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast Cancer; Necrosis; Tamoxifen; Thymoquinone.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Low Doses of Thymoquinone and Ferulic Acid in Combination Effectively Inhibit Proliferation of Cultured MDA-MB 231 Breast Adenocarcinoma Cells.Nutr Cancer. 2021;73(2):282-289. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2020.1743869. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Nutr Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32223348
-
Thymoquinone anticancer activity is enhanced when combined with royal jelly in human breast cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2021 May 24;12(5):342-354. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i5.342. World J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34131566 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Aneuploidy Induction Contribute to Thymoquinone Anticancer Activity.Molecules. 2021 Aug 25;26(17):5136. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175136. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500570 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone, as a Novel Therapeutic Candidate of Cancers.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Apr 16;14(4):369. doi: 10.3390/ph14040369. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymoquinone in the clinical treatment of cancer: Fact or fiction?Pharmacogn Rev. 2013 Jul;7(14):117-20. doi: 10.4103/0973-7847.120509. Pharmacogn Rev. 2013. PMID: 24347919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic evaluation of phytochemicals in breast cancer remedy: current understanding and future perspectives.RSC Adv. 2018 Aug 22;8(52):29714-29744. doi: 10.1039/c8ra04879g. eCollection 2018 Aug 20. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35547279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment of Breast Cancer.Nutrients. 2017 Jul 8;9(7):728. doi: 10.3390/nu9070728. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28698459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymoquinone Is a Multitarget Single Epidrug That Inhibits the UHRF1 Protein Complex.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 22;12(5):622. doi: 10.3390/genes12050622. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymoquinone Enhances Paclitaxel Anti-Breast Cancer Activity via Inhibiting Tumor-Associated Stem Cells Despite Apparent Mathematical Antagonism.Molecules. 2020 Jan 20;25(2):426. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020426. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31968657 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the nutriceutics in early-stage breast cancer: mechanisms, combinational therapy, and drug delivery.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Sep 18;22(1):574. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02815-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39294665 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Osborne CK. Tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1609–1618. - PubMed
-
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(3):205–213. - PubMed
-
- Osborne CK, Bardou V, Hopp TA, Chamness GC, Hilsenbeck SG, Fuqua SA, et al. Role of the estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 (SRC-3) and HER2/neu in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95(5):353–361. - PubMed
-
- Jeng MH, Jordan VC. Growth stimulation and differential regulation of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF beta 1), TGF beta 2, and TGF beta 3 messenger RNA levels by norethindrone in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991;5(8):1120–1128. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
