An imaging-based approach predicts clinical outcomes in prostate cancer through a novel support vector machine classification
- PMID: 27542201
- PMCID: PMC5363650
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11293
An imaging-based approach predicts clinical outcomes in prostate cancer through a novel support vector machine classification
Abstract
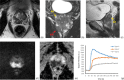
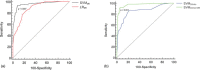
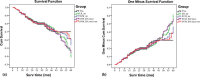
Preoperatively predict the probability of Prostate cancer (PCa) biochemical recurrence (BCR) is of definite clinical relevance. The purpose of this study was to develop an imaging-based approach in the prediction of 3-years BCR through a novel support vector machine (SVM) classification. We collected clinicopathologic and MR imaging datasets in 205 patients pathologically confirmed PCa after radical prostatectomy. Univariable and multivariable analyses were used to assess the association between MR findings and 3-years BCR, and modeled the imaging variables and follow-up data to predict 3-year PCa BCR using SVM analysis. The performance of SVM was compared with conventional Logistic regression (LR) and D'Amico risk stratification scheme by area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (Az) analysis. We found that SVM had significantly higher Az (0.959 vs. 0.886; p = 0.007), sensitivity (93.3% vs. 83.3%; p = 0.025), specificity (91.7% vs. 77.2%; p = 0.009) and accuracy (92.2% vs. 79.0%; p = 0.006) than LR analysis. Performance of popularized D'Amico scheme was effectively improved by adding MRI-derived variables (Az: 0.970 vs. 0.859, p < 0.001; sensitivity: 91.7% vs. 86.7%, p = 0.031; specificity: 94.5% vs. 78.6%, p = 0.001; and accuracy: 93.7% vs. 81.0%, p = 0.007). Additionally, beside pathological Gleason score (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.560, p = 0.008), surgical-T3b (HR = 4.525, p < 0.001) and positive surgical margin (HR = 1.314, p = 0.007), apparent diffusion coefficient (HR = 0.149, p = 0.035) was the only independent imaging predictor of time to PSA failure. Therefore, We concluded that imaging-based approach using SVM was superior to LR analysis in predicting PCa outcome. Adding MR variables improved the performance of D'Amico scheme.
Keywords: MRI; biochemical recurrence; prostate cancer; radical prostatectomy; support vector machine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, van der Kwast T, Mason M, Matveev V, Wiegel T, Zattoni F, Mottet N, European Association of U. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. European urology. 2014;65(2):467–479. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, van der Kwast T, Mason M, Matveev V, Wiegel T, Zattoni F, Mottet N, European Association of U. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent-update 2013. European urology. 2014;65(1):124–137. - PubMed
-
- Abdollah F, Boorjian S, Cozzarini C, Suardi N, Sun M, Fiorino C, di Muzio N, Karakiewicz PI, Montorsi F, Karnes RJ, Briganti A. Survival following biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy and adjuvant radiotherapy in patients with prostate cancer: the impact of competing causes of mortality and patient stratification. European urology. 2013;64(4):557–564. - PubMed
-
- Rigatti P, Suardi N, Briganti A, Da Pozzo LF, Tutolo M, Villa L, Gallina A, Capitanio U, Abdollah F, Scattoni V, Colombo R, Freschi M, Picchio M, Messa C, Guazzoni G, Montorsi F. Pelvic/retroperitoneal salvage lymph node dissection for patients treated with radical prostatectomy with biochemical recurrence and nodal recurrence detected by [11C]choline positron emission tomography/computed tomography. European urology. 2011;60(5):935–943. - PubMed
-
- Capitanio U, Scattoni V, Freschi M, Briganti A, Salonia A, Gallina A, Colombo R, Karakiewicz PI, Rigatti P, Montorsi F. Radical prostatectomy for incidental (stage T1a-T1b) prostate cancer: analysis of predictors for residual disease and biochemical recurrence. European urology. 2008;54(1):118–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

