Antineoplastic effects and mechanisms of micheliolide in acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells
- PMID: 27542251
- PMCID: PMC5323134
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11342
Antineoplastic effects and mechanisms of micheliolide in acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells
Abstract
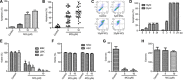
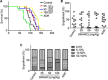
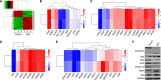
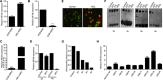
Leukemic stem cells (LSCs) greatly contribute to the initiation, relapse, and multidrug resistance of leukemia. Current therapies targeting the cell cycle and rapidly growing leukemic cells, including conventional chemotherapy, have little effect due to the self-renewal and differentiated malignant cells replenishment ability of LSCs despite their scarce supply in the bone marrow. Micheliolide (MCL) is a natural guaianolide sesquiterpene lactone (GSL) which was discovered in michelia compressa and michelia champaca plants, and has been shown to exert selective cytotoxic effects on CD34+CD38- LSCs. In this study, we demonstrate that DMAMCL significantly prolongs the lifespan of a mouse model of human acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Mechanistic investigations further revealed that MCL exerted its cytotoxic effects via inhibition of NF-κB expression and activity, and by generating intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). These results provide valuable insight into the mechanisms underlying MCL-induced cytotoxicity of LSCs, and support further preclinical investigations of MCL-related therapies for the treatment of AML.
Keywords: leukemic stem cells; micheliolide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Guaianolide sesquiterpene lactones, a source to discover agents that selectively inhibit acute myelogenous leukemia stem and progenitor cells.J Med Chem. 2012 Oct 25;55(20):8757-69. doi: 10.1021/jm301064b. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22985027
-
The sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide induces apoptosis of human acute myelogenous leukemia stem and progenitor cells.Blood. 2005 Jun 1;105(11):4163-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-4135. Epub 2005 Feb 1. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15687234 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfiram/copper selectively eradicates AML leukemia stem cells in vitro and in vivo by simultaneous induction of ROS-JNK and inhibition of NF-κB and Nrf2.Cell Death Dis. 2017 May 18;8(5):e2797. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.176. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28518151 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of TIM-3 as a Leukemic Stem Cell Surface Molecule in Primary Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Oncology. 2015;89 Suppl 1:28-32. doi: 10.1159/000431062. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Oncology. 2015. PMID: 26551150 Review.
-
Targeting LSCs through membrane antigens selectively or preferentially expressed on these cells.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2015 Dec;55(4):336-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2015.07.015. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2015. PMID: 26460257 Review.
Cited by
-
Peperomin E and its orally bioavailable analog induce oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells by targeting thioredoxin reductase.Redox Biol. 2019 Jun;24:101153. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101153. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30909158 Free PMC article.
-
Antineoplastic effects of CPPTL via the ROS/JNK pathway in acute myeloid leukemia.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 13;8(24):38990-39000. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17166. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28473664 Free PMC article.
-
iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics analysis of the effect of ACT001 on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 13;13(1):11336. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38448-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37443174 Free PMC article.
-
Micheliolide exerts effects in myeloproliferative neoplasms through inhibiting STAT3/5 phosphorylation via covalent binding to STAT3/5 proteins.Blood Sci. 2023 Jul 12;5(4):258-268. doi: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000168. eCollection 2023 Oct. Blood Sci. 2023. PMID: 37941916 Free PMC article.
-
Plant sesquiterpene lactones.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Nov 18;379(1914):20230350. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0350. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39343024 Review.
References
-
- Jamieson CH, Ailles LE, Dylla SJ, Muijtjens M, Jones C, Zehnder JL, Gotlib J, Li K, Manz MG, Keating A, Sawyers CL, Weissman IL. Granulocyte-macrophage progenitors as candidate leukemic stem cells in blast-crisis CML. The New England journal of medicine. 2004;351:657–667. - PubMed
-
- Thomas D, Majeti R. Burning Fat Fuels Leukemic Stem Cell Heterogeneity. Cell stem cell. 2016;19:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Ramdass B, Chowdhary A, Koka PS. Hematological malignancies: disease pathophysiology of leukemic stem cells. Journal of stem cells. 2013;8:151–187. - PubMed
-
- Quek L, Otto GW, Garnett C, Lhermitte L, Karamitros D, Stoilova B, Lau IJ, Doondeea J, Usukhbayar B, Kennedy A, Metzner M, Goardon N, Ivey A, et al. Genetically distinct leukemic stem cells in human CD34-acute myeloid leukemia are arrested at a hemopoietic precursor-like stage. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2016 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bjerkvig R, Tysnes BB, Aboody KS, Najbauer J, Terzis AJ. Opinion: the origin of the cancer stem cell: current controversies and new insights. Nature reviews Cancer. 2005;5:899–904. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

