Sorafenib inhibits cell growth but fails to enhance radio- and chemosensitivity of glioblastoma cell lines
- PMID: 27542273
- PMCID: PMC5308705
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11328
Sorafenib inhibits cell growth but fails to enhance radio- and chemosensitivity of glioblastoma cell lines
Abstract
Background: Glioblastomas (GBM) are the most common malignant type of primary brain tumor. GBM are intensively treated with surgery and combined radiochemotherapy using X-irradiation and temozolomide (TMZ) but they are still associated with an extremely poor prognosis, urging for the development of new treatment strategies. To improve the outcome of GBM patients, the small molecule multi-kinase inhibitor sorafenib has moved into focus of recent research. Sorafenib has already been shown to enhance the radio- and radiochemosensitivity of other tumor entities. Whether sorafenib is also able to sensitize GBM cells to radio- and chemotherapy is still an unsolved question which we have addressed in this study.
Methods: The effect of sorafenib on signaling, proliferation, radiosensitivity, chemosensitivity and radiochemosensitivity was analyzed in six glioblastoma cell lines using Western blot, proliferation- and colony formation assays.
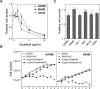
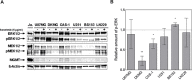
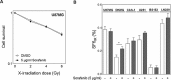
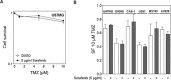
Results: In half of the cell lines sorafenib clearly inhibited MAPK signaling. We also observed a strong blockage of proliferation, which was, however, not associated with MAPK pathway inhibition. Sorafenib had only minor effects on cell survival when administered alone. Most importantly, sorafenib treatment failed to enhance GBM cell killing by irradiation, TMZ or combined treatment, and instead rather caused resistance in some cell lines.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that sorafenib treatment may not improve the efficacy of radiochemotherapy in GBM.
Keywords: X-irradiation; glioblastoma; radiochemosensitivity; sorafenib; temozolomide.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Autophagy by Chloroquine Enhances the Antitumor Efficacy of Sorafenib in Glioblastoma.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;36(7):1197-208. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0318-z. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26971793 Free PMC article.
-
Sorafenib selectively depletes human glioblastoma tumor-initiating cells from primary cultures.Cell Cycle. 2013 Feb 1;12(3):491-500. doi: 10.4161/cc.23372. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23324350 Free PMC article.
-
Sorafenib plus daily low-dose temozolomide for relapsed glioblastoma: a phase II study.Anticancer Res. 2013 Aug;33(8):3487-94. Anticancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23898124 Clinical Trial.
-
Targeted treatment of ovarian cancer--the multiple - kinase - inhibitor sorafenib as a potential option.Anticancer Res. 2014 Apr;34(4):1519-30. Anticancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24692678 Review.
-
Novel therapies hijack the blood-brain barrier to eradicate glioblastoma cancer stem cells.Carcinogenesis. 2019 Mar 12;40(1):2-14. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy171. Carcinogenesis. 2019. PMID: 30475990 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress Activated by Sorafenib Alters the Temozolomide Sensitivity of Human Glioma Cells Through Autophagy and JAK2/STAT3-AIF Axis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 14;9:660005. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.660005. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34277607 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Role of Endothelial Cells in Glioblastoma: Mechanisms and Novel Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 1;25(11):6118. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116118. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of FDA-Approved Multi-Target Angiogenesis Drugs for Brain Tumor Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 28;26(5):2192. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052192. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glioblastoma and acute myeloid leukemia: malignancies with striking similarities.J Neurooncol. 2018 Jan;136(2):223-231. doi: 10.1007/s11060-017-2676-5. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Neurooncol. 2018. PMID: 29196926 Review.
-
MiR-374b re-sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib therapy by antagonizing PKM2-mediated glycolysis pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 1;9(4):765-778. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31106002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm S, Carter C, Lynch M, Lowinger T, Dumas J, Smith RA, Schwartz B, Simantov R, Kelley S. Discovery and development of sorafenib: a multikinase inhibitor for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:835–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

