Conditional ablation of HDAC3 in islet beta cells results in glucose intolerance and enhanced susceptibility to STZ-induced diabetes
- PMID: 27542279
- PMCID: PMC5295367
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11295
Conditional ablation of HDAC3 in islet beta cells results in glucose intolerance and enhanced susceptibility to STZ-induced diabetes
Abstract
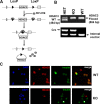
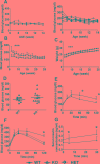
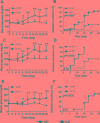
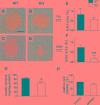
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are enzymes that regulate gene expression by modifying chromatin structure through removal of acetyl groups from target histones or non-histone proteins. Previous in vitro studies suggest that HDACs may be novel pharmacological targets in immune-mediated islet β-cell destruction. However, the role of specific HDAC in islet β-cell development and function remain unclear. Here, we generated a conditional islet β-cells specific HDAC3 deletion mouse model to determine the consequences of HDAC3 depletion on islet β-cell differentiation, maintenance and function. Islet morphology, insulin secretion, glucose tolerance, and multiple low-dose streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes incidence were evaluated and compared between HDAC3 knockout and wild type littermate controls. Mice with β-cell-specific HDAC3 deletion displayed decreased pancreatic insulin content, disrupted glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, with intermittent spontaneous diabetes and dramatically enhanced susceptibility to STZ-induced diabetes. Furthermore, islet β-cell line, MIN6 cells with siRNA-mediated HDAC3 silence, showed decreased insulin gene transcription, which was mediated, at least partially, through the upregulation of suppressors of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3). These results indicate the critical role of HDAC3 in normal β-cell differentiation, maintenance and function.
Keywords: HDAC3; Pathology Section; autoimmune diabetes; glucose tolerance; insulin; knockout.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTREST The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deletion of histone deacetylase 3 in adult beta cells improves glucose tolerance via increased insulin secretion.Mol Metab. 2016 Nov 22;6(1):30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2016.11.007. eCollection 2017 Jan. Mol Metab. 2016. PMID: 28123935 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT6-mediated transcriptional suppression of Txnip is critical for pancreatic beta cell function and survival in mice.Diabetologia. 2018 Apr;61(4):906-918. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4542-6. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29322219 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 3-selective inhibitor RGFP966 ameliorates impaired glucose tolerance through β-cell protection.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 1;406:115189. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115189. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32800772
-
Pharmacological treatment of chronic diabetes by stimulating pancreatic beta-cell regeneration with systemic co-administration of EGF and gastrin.Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002 Dec;91(6):414-20. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0773.2002.910621.x. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 12688387 Review.
-
Trophic stimulation of the ductular-islet cell axis: a new approach to the treatment of diabetes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;321:95-104; discussion 105-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3448-8_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992. PMID: 1449087 Review.
Cited by
-
The Emerging Role of HDACs: Pathology and Therapeutic Targets in Diabetes Mellitus.Cells. 2021 May 28;10(6):1340. doi: 10.3390/cells10061340. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34071497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of histone deacetylase 3 in adult beta cells improves glucose tolerance via increased insulin secretion.Mol Metab. 2016 Nov 22;6(1):30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2016.11.007. eCollection 2017 Jan. Mol Metab. 2016. PMID: 28123935 Free PMC article.
-
Microdose Lithium Protects against Pancreatic Islet Destruction and Renal Impairment in Streptozotocin-Elicited Diabetes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jan 19;10(1):138. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010138. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33478120 Free PMC article.
-
A whole organism small molecule screen identifies novel regulators of pancreatic endocrine development.Development. 2019 Jul 24;146(14):dev172569. doi: 10.1242/dev.172569. Development. 2019. PMID: 31142539 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose metabolism partially regulates β-cell function through epigenomic changes.J Diabetes Investig. 2024 Jun;15(6):649-655. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14173. Epub 2024 Mar 4. J Diabetes Investig. 2024. PMID: 38436511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grunstein M. Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature. 1997;389(6649):349–352. - PubMed
-
- Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML, Rehman M, Walther TC, Olsen JV, Mann M. Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science. 2009;325(5942):834–840. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

