Exocytosis of polyubiquitinated proteins in bortezomib-resistant leukemia cells: a role for MARCKS in acquired resistance to proteasome inhibitors
- PMID: 27542283
- PMCID: PMC5342701
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11340
Exocytosis of polyubiquitinated proteins in bortezomib-resistant leukemia cells: a role for MARCKS in acquired resistance to proteasome inhibitors
Abstract
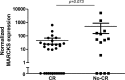
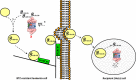
PSMB5 mutations and upregulation of the β5 subunit of the proteasome represent key determinants of acquired resistance to the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (BTZ) in leukemic cells in vitro. We here undertook a multi-modality (DNA, mRNA, miRNA) array-based analysis of human CCRF-CEM leukemia cells and BTZ-resistant subclones to determine whether or not complementary mechanisms contribute to BTZ resistance. These studies revealed signatures of markedly reduced expression of proteolytic stress related genes in drug resistant cells over a broad range of BTZ concentrations along with a high upregulation of myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) gene expression. MARCKS upregulation was confirmed on protein level and also observed in other BTZ-resistant tumor cell lines as well as in leukemia cells with acquired resistance to other proteasome inhibitors. Moreover, when MARCKS protein expression was demonstrated in specimens derived from therapy-refractory pediatric leukemia patients (n = 44), higher MARCKS protein expression trended (p = 0.073) towards a dismal response to BTZ-containing chemotherapy. Mechanistically, we show a BTZ concentration-dependent association of MARCKS protein levels with the emergence of ubiquitin-containing vesicles in BTZ-resistant CEM cells. These vesicles were found to be extruded and taken up in co-cultures with proteasome-proficient acceptor cells. Consistent with these observations, MARCKS protein associated with ubiquitin-containing vesicles was also more prominent in clinical leukemic specimen with ex vivo BTZ resistance compared to BTZ-sensitive leukemia cells. Collectively, we propose a role for MARCKS in a novel mechanism of BTZ resistance via exocytosis of ubiquitinated proteins in BTZ-resistant cells leading to quenching of proteolytic stress.
Keywords: MARCKS; bortezomib; leukemia; proteasome; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this manuscript.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antileukemic activity and mechanism of drug resistance to the marine Salinispora tropica proteasome inhibitor salinosporamide A (Marizomib).Mol Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;86(1):12-9. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.092114. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Mol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24737138 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired bortezomib binding to mutant β5 subunit of the proteasome is the underlying basis for bortezomib resistance in leukemia cells.Leukemia. 2012 Apr;26(4):757-68. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.256. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Leukemia. 2012. PMID: 21941364
-
Anti-leukemic activity and mechanisms underlying resistance to the novel immunoproteasome inhibitor PR-924.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 May 1;89(1):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.02.005. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24552657
-
The preclinical discovery and development of bortezomib for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017 Feb;12(2):225-235. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2017.1268596. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 27917682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(Immuno)proteasomes as therapeutic target in acute leukemia.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017 Dec;36(4):599-615. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9699-4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017. PMID: 29071527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from ascitic fluid enhance growth and migration of ovarian cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 28;11(1):9149. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88163-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33911091 Free PMC article.
-
Increased MARCKS Activity in BRAF Inhibitor-Resistant Melanoma Cells Is Essential for Their Enhanced Metastatic Behavior Independent of Elevated WNT5A and IL-6 Signaling.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 10;14(24):6077. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246077. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551563 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-Clinical Evaluation of the Proteasome Inhibitor Ixazomib against Bortezomib-Resistant Leukemia Cells and Primary Acute Leukemia Cells.Cells. 2021 Mar 17;10(3):665. doi: 10.3390/cells10030665. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33802801 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of the Response to Conventional Chemotherapeutics in Pro-B-ALL Cell Lines in Terms of Tumor Relapse.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jul 14;13(7):1240. doi: 10.3390/genes13071240. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35886023 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological roles of myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) in hematological malignancies.Biomark Res. 2021 May 6;9(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00286-9. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 33958003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Niewerth D, Dingjan I, Cloos J, Jansen G, Kaspers G. Proteasome inhibitors in acute leukemia. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2013;13:327–337. - PubMed
-
- Crawford LJ, Walker B, Ovaa H, Chauhan D, Anderson KC, Morris TC, Irvine AE. Comparative selectivity and specificity of the proteasome inhibitors BzLLLCOCHO, PS-341, and MG-132. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6379–6386. - PubMed
-
- Ruschak AM, Slassi M, Kay LE, Schimmer AD. Novel proteasome inhibitors to overcome bortezomib resistance. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:1007–1017. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

