Development and Validation of a Sudden Cardiac Death Prediction Model for the General Population
- PMID: 27542394
- PMCID: PMC5021600
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.023042
Development and Validation of a Sudden Cardiac Death Prediction Model for the General Population
Abstract
Background: Most sudden cardiac death (SCD) events occur in the general population among persons who do not have any prior history of clinical heart disease. We sought to develop a predictive model of SCD among US adults.
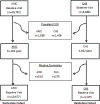
Methods: We evaluated a series of demographic, clinical, laboratory, electrocardiographic, and echocardiographic measures in participants in the ARIC study (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities) (n=13 677) and the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study) (n=4207) who were free of baseline cardiovascular disease. Our initial objective was to derive a SCD prediction model using the ARIC cohort and validate it in CHS. Independent risk factors for SCD were first identified in the ARIC cohort to derive a 10-year risk model of SCD. We compared the prediction of SCD with non-SCD and all-cause mortality in both the derivation and validation cohorts. Furthermore, we evaluated whether the SCD prediction equation was better at predicting SCD than the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Cardiovascular Disease Pooled Cohort risk equation.
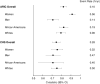
Results: There were a total of 345 adjudicated SCD events in our analyses, and the 12 independent risk factors in the ARIC study included age, male sex, black race, current smoking, systolic blood pressure, use of antihypertensive medication, diabetes mellitus, serum potassium, serum albumin, high-density lipoprotein, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and QTc interval. During a 10-year follow-up period, a model combining these risk factors showed good to excellent discrimination for SCD risk (c-statistic 0.820 in ARIC and 0.745 in CHS). The SCD prediction model was slightly better in predicting SCD than the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Pooled Cohort risk equations (c-statistic 0.808 in ARIC and 0.743 in CHS). Only the SCD prediction model, however, demonstrated similar and accurate prediction for SCD using both the original, uncalibrated score and the recalibrated equation. Finally, in the echocardiographic subcohort, a left ventricular ejection fraction <50% was present in only 1.1% of participants and did not enhance SCD prediction.
Conclusions: Our study is the first to derive and validate a generalizable risk score that provides well-calibrated, absolute risk estimates across different risk strata in an adult population of white and black participants without a clinical diagnosis of cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: arrhythmia; population; risk prediction; sudden cardiac death.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
Letter by Fysekidis et al Regarding Article, "Development and Validation of a Sudden Cardiac Death Prediction Model for the General Population".Circulation. 2017 Mar 7;135(10):e634-e635. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025924. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28264893 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Karam et al Regarding Article, "Development and Validation of a Sudden Cardiac Death Prediction Model for the General Population".Circulation. 2017 Mar 7;135(10):e636-e637. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026081. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28264894 No abstract available.
-
Response by Deo et al to Letters Regarding Article, "Development and Validation of a Sudden Cardiac Death Prediction Model for the General Population".Circulation. 2017 Mar 7;135(10):e638-e639. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027080. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28264895 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fishman GI, Chugh SS, Dimarco JP, Albert CM, Anderson ME, Bonow RO, Buxton AE, Chen P-S, Estes M, Jouven X, Kwong R, Lathrop DA, Mascette AM, Nerbonne JM, O’Rourke B, Page RL, Roden DM, Rosenbaum DS, Sotoodehnia N, Trayanova NA, Zheng ZJ. Sudden cardiac death prediction and prevention: report from a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Heart Rhythm Society Workshop. Circulation. 2010;122:2335–2348. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moss AJ, Zareba W, Hall WJ, Klein H, Wilber DJ, Cannom DS, Daubert JP, Higgins SL, Brown MW, Andrews ML. Prophylactic implantation of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:877–883. - PubMed
-
- Chugh SS, Jui J, Gunson K, Stecker EC, John BT, Thompson B, Ilias N, Vickers C, Dogra V, Daya M, Kron J, Zheng ZJ, Mensah G, McAnulty J. Current burden of sudden cardiac death: multiple source surveillance versus retrospective death certificate-based review in a large U.S. community. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:1268–1275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL099452/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK089118/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111089/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

