2-Cys peroxiredoxin is required in successful blood-feeding, reproduction, and antioxidant response in the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis
- PMID: 27542835
- PMCID: PMC4992251
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-016-1748-2
2-Cys peroxiredoxin is required in successful blood-feeding, reproduction, and antioxidant response in the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis
Abstract
Background: Ticks are obligate hematophagous arthropods that feed on vertebrate blood that contains iron. Ticks also concentrate host blood with iron; this concentration of the blood leads to high levels of iron in ticks. The host-derived iron reacts with oxygen in the tick body and this may generate high levels of reactive oxygen species, including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). High levels of H2O2 cause oxidative stress in organisms and therefore, antioxidant responses are necessary to regulate H2O2. Here, we focused on peroxiredoxin (Prx), an H2O2-scavenging enzyme in the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis.
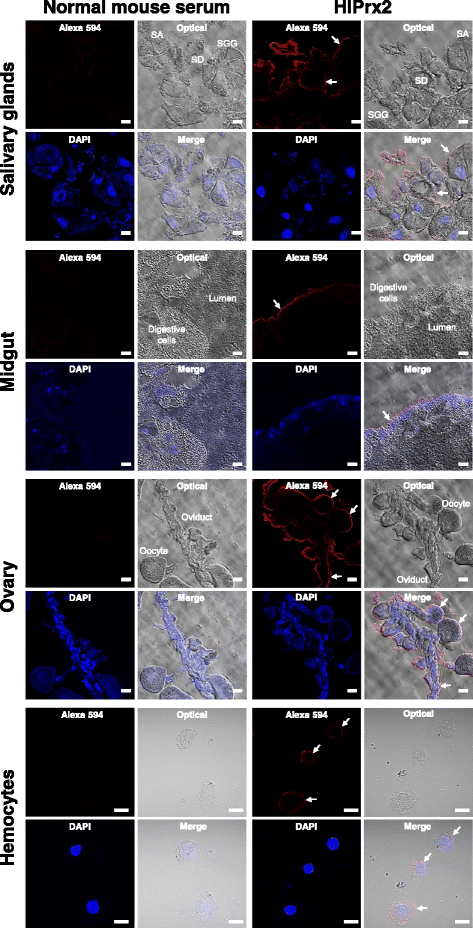
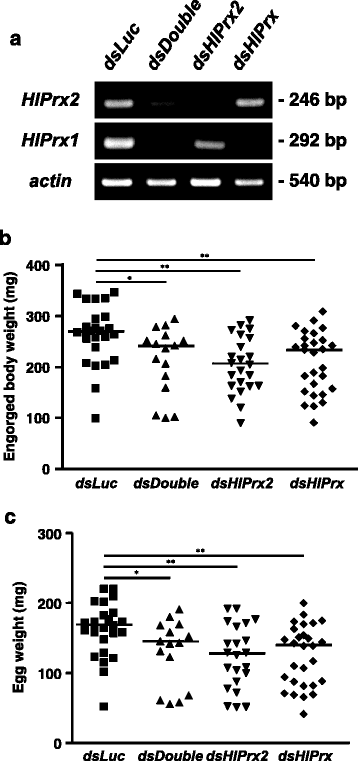
Methods: The mRNA and protein expression profiles of 2-Cys peroxiredoxin (HlPrx2) in H. longicornis were investigated in whole ticks and internal organs, and developmental stages, using real-time PCR and Western blot analysis during blood-feeding. The localization of HlPrx2 proteins in tick tissues was also observed by immunostaining. Moreover, knockdown experiments of HlPrx2 were performed using RNA interference to evaluate its function in ticks.
Results: Real-time PCR showed that HlPrx2 gene expression in whole ticks and internal organs was significantly upregulated by blood-feeding. However, protein expression, except in the midgut, was constant throughout blood-feeding. Knockdown of the HlPrx2 gene caused significant differences in the engorged body weight, egg weight and hatching rate for larvae as compared to the control group. Finally, detection of H2O2 after knockdown of HlPrxs in ticks showed that the concentration of H2O2 significantly increased before and after blood-feeding.
Conclusion: Therefore, HlPrx2 can be considered important for successful blood-feeding and reproduction through the regulation of H2O2 concentrations in ticks before and after blood-feeding. This study contributes to the search for a candidate target for tick control and further understanding of the tick's oxidative stress coping mechanism during blood-feeding.
Keywords: Haemaphysalis longicornis; Hydrogen peroxide; Peroxiredoxin; RNA interference.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Peroxiredoxin From the Haemaphysalis longicornis Tick Affects Langat Virus Replication in a Hamster Cell Line.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jan 28;10:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00007. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32047725 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple roles of peroxiredoxins in tick blood feeding.Exp Appl Acarol. 2018 Jul;75(3):269-280. doi: 10.1007/s10493-018-0273-8. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Exp Appl Acarol. 2018. PMID: 30030662 Review.
-
Functional analysis of recombinant 2-Cys peroxiredoxin from the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis.Insect Mol Biol. 2016 Feb;25(1):16-23. doi: 10.1111/imb.12193. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Insect Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26471013
-
Characterization and expression analysis of a newly identified glutathione S-transferase of the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis during blood-feeding.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Feb 8;11(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2667-1. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 29422079 Free PMC article.
-
Biology, ecology and distribution of the tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann (Acari: Ixodidae) in New Zealand.N Z Vet J. 2016 Jan;64(1):10-20. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2015.1035769. Epub 2015 Jun 23. N Z Vet J. 2016. PMID: 25849758 Review.
Cited by
-
Twenty-four-hour ambulatory oximetry monitoring in a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis for assisting in the discharge instruction on activities of daily living: a case report.J Phys Ther Sci. 2020 Nov;32(11):768-771. doi: 10.1589/jpts.32.768. Epub 2020 Nov 11. J Phys Ther Sci. 2020. PMID: 33281294 Free PMC article.
-
A Peroxiredoxin From the Haemaphysalis longicornis Tick Affects Langat Virus Replication in a Hamster Cell Line.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jan 28;10:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00007. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32047725 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired tick resistance: The trail is hot.Parasite Immunol. 2021 May;43(5):e12808. doi: 10.1111/pim.12808. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Parasite Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33187012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multiple roles of peroxiredoxins in tick blood feeding.Exp Appl Acarol. 2018 Jul;75(3):269-280. doi: 10.1007/s10493-018-0273-8. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Exp Appl Acarol. 2018. PMID: 30030662 Review.
-
The redox metabolic pathways function to limit Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection and multiplication while preserving fitness in tick vector cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 13;9(1):13236. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49766-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31520000 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

