The effects of dopamine receptor 2 expression on B cells on bone metabolism and TNF-α levels in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 27542839
- PMCID: PMC4992283
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-1220-7
The effects of dopamine receptor 2 expression on B cells on bone metabolism and TNF-α levels in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Dopamine receptor 2 (DR2) expressions on B cells from Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients has been found to be negatively correlated with disease activity and can potentially predict the response to treatment. This study aimed to investigate the role of B cell DR2 expression on bone remodeling in RA.
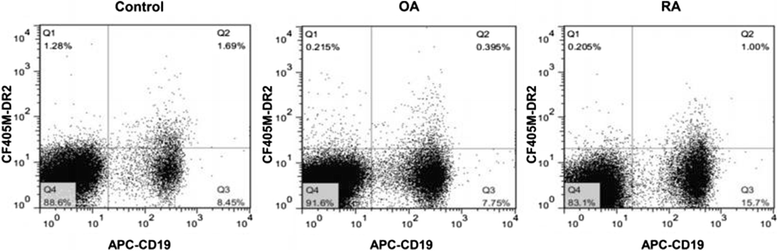
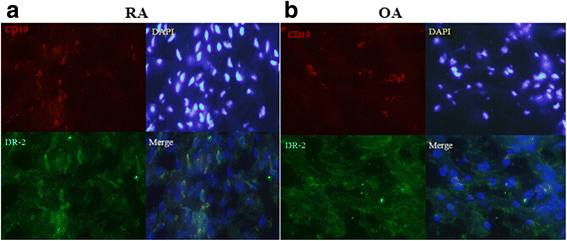
Methods: Patients with RA (n = 14) or osteoarthritis (OA; n = 12), and healthy controls (n = 12) were recruited for this study. Dopamine receptor (DR) 2 expression was assessed using flow cytometry. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleuin(IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-17, and tumor necrosis factor(TNF)-α, and bone turnovers, including osteocalcin (OC),serum procollagen type I N propeptide (PINP), C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (β-CTX), collagen type I cross-linked telopeptide (ICTP), as well as matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) and osteoprotegerin (OPG) were measured by electrochemiluminescence, chemiluminescence, or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. DR2 expression on synovial B cells from 4 RA patients and 3 OA patients was detected by immunofluorescence.
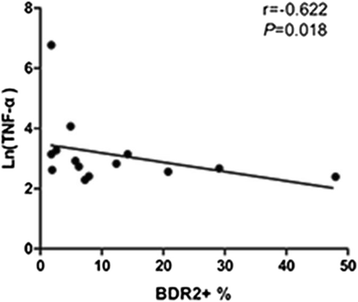
Results: There were more DR2(+)CD19(+) B cells in synovial tissues from RA patients than in those from OA patients. The frequency of peripheral B cells that expressed DR2 was positively correlated with plasma TNF-α level. Levels of ICTP and MMP-3 were significantly higher, and OPG were lower in RA patients compared to those in the OA group and healthy controls (all P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The frequency of B cells that expressed DR2 showed a correlation with levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α. DR2(+)CD19(+) B cells in synovial tissues might have a role in bone metabolism and TNF-α production.
Keywords: B cells; Bone metabolism; Dopamine receptor; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dopamine receptor DR2 expression in B cells is negatively correlated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Immunobiology. 2015 Mar;220(3):323-30. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.10.016. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Immunobiology. 2015. PMID: 25468566
-
Periarticular bone gain at proximal interphalangeal joints and changes in bone turnover markers in response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2013 May;40(5):653-62. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.120397. Epub 2013 Mar 1. J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23457381
-
Soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-2 in serum and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis and osteoarthritis.J Rheumatol. 1995 Mar;22(3):406-12. J Rheumatol. 1995. PMID: 7783054
-
The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology.Biorheology. 2002;39(1-2):237-46. Biorheology. 2002. PMID: 12082286 Review.
-
B Lymphocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Effects of Anti-TNF-α Agents on B Lymphocytes: A Review of the Literature.Clin Ther. 2018 Jun;40(6):1034-1045. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.04.016. Epub 2018 May 23. Clin Ther. 2018. PMID: 29801753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of a ceRNA Network Related to Rheumatoid Arthritis.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 6;13(4):647. doi: 10.3390/genes13040647. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456453 Free PMC article.
-
Dopaminergic Agents in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;15(1):48-56. doi: 10.1007/s11481-019-09850-5. Epub 2019 Apr 23. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31016462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated administration of mazindol reduces spontaneous pain-related behaviors without modifying bone density and microarchitecture in a mouse model of complete Freund's adjuvant-induced knee arthritis.J Pain Res. 2017 Jul 27;10:1777-1786. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S136581. eCollection 2017. J Pain Res. 2017. PMID: 28794657 Free PMC article.
-
CysLT1 receptor antagonist alleviates pathogenesis of collagen-induced arthritis mouse model.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 26;8(65):108418-108429. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22664. eCollection 2017 Dec 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29312540 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of inflammatory biomarkers in the peri-implant crevicular fluid before and after the occlusal loading of narrow diameter implants.Clin Oral Investig. 2020 Mar;24(3):1311-1320. doi: 10.1007/s00784-019-03010-y. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Clin Oral Investig. 2020. PMID: 31312971
References
-
- Jones SM, Bhalla AK. Osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1993;11:557–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

