High Prevalence of Diverse Insertion Sequences within the rRNA Operons of Mycoplasma bovis
- PMID: 27542937
- PMCID: PMC5066355
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01628-16
High Prevalence of Diverse Insertion Sequences within the rRNA Operons of Mycoplasma bovis
Abstract
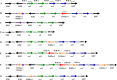
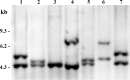
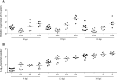
Insertion sequences (ISs) are widespread in the genome of Mycoplasma bovis strain PG45, but no ISs were identified within its two tandemly positioned rRNA operons (rrn1 and rrn2). However, characterization of the rrn locus in 70 M. bovis isolates revealed the presence of ISs related to the ISMbov1 (IS30 family) and ISMbov4 (IS4 family) isomers in 35 isolates. ISs were inserted into intergenic region 1 (IGR-1) or IGR-3, which are the putative promoter regions of rrn1 and rrn2, respectively, and into IGR-5, located downstream of the rrl2 gene. Seven different configurations (A to G) of the rrn locus with respect to ISs were identified, including those in five annotated genomes. The transcriptional start site for the single rrn operon in M. bovis strain 88127 was mapped within IGR-1, 60 bp upstream of the rrs gene. Notably, only 1 nucleotide separated the direct repeat (DR) for ISMbov1 and the promoter -35 element in configuration D, while in configuration F, the -35 motif was a part of the ISMbov1 DR. Relative quantitative real-time (qRT) PCR analysis and growth rate comparisons detected a significant increase (P < 0.05) in the expression of the rrs genes and in the number of viable cells during log phase growth (8, 12, and 16 h) in the strains with configuration F in comparison to strains with one or two rrn operons that did not have ISs. A high prevalence of IS elements within or close to the M. bovis rrn operon-promoter region may reflect their important role in regulation of both ribosome synthesis and function.
Importance: Data presented in this study show a high prevalence of diverse ISs within the M. bovis rrn locus resulting in intraspecies variability and diversity. Such abundance of IS elements near or within the rrn locus may offer a selective advantage to M. bovis Moreover, the fact that expression of the rrs genes as well as the number of viable cells increased in the group of strains with IS element insertion within a putative promoter -35 sequence (configuration F) in comparison to that in strains with one or two rrn operons that do not have ISs may serve as a basis for understanding the possible role of M. bovis IS elements in fundamental biological processes such as regulation of ribosome synthesis and function.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of newly identified IS3, IS4 and IS30 insertion sequence-like elements in Mycoplasma bovis and their possible roles in genome plasticity.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009 May;294(2):172-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01562.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19416360
-
Mycoplasma bovis shares insertion sequences with Mycoplasma agalactiae and Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides SC: Evolutionary and developmental aspects.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005 Apr 15;245(2):249-55. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.03.013. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005. PMID: 15837379
-
Comparative and functional analysis of the rRNA-operons and their tRNA gene complement in different lactic acid bacteria.Syst Appl Microbiol. 2006 Jul;29(5):358-67. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2005.11.010. Epub 2005 Dec 9. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16338113
-
Reprint of New opportunities for improved ribotyping of C. difficile clinical isolates by exploring their genomes.J Microbiol Methods. 2013 Dec;95(3):425-40. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2013.09.009. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Microbiol Methods. 2013. PMID: 24050948 Review.
-
New opportunities for improved ribotyping of C. difficile clinical isolates by exploring their genomes.J Microbiol Methods. 2013 Jun;93(3):257-72. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2013.02.013. Epub 2013 Mar 29. J Microbiol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23545446 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations Associated with Decreased Susceptibility to Seven Antimicrobial Families in Field and Laboratory-Derived Mycoplasma bovis Strains.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jan 24;61(2):e01983-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01983-16. Print 2017 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 27895010 Free PMC article.
-
A GC-Rich Prophage-Like Genomic Region of Mycoplasma bovirhinis HAZ141_2 Carries a Gene Cluster Encoding Resistance to Kanamycin and Neomycin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Jan 20;65(2):e01010-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01010-20. Print 2021 Jan 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33257452 Free PMC article.
-
High quality genome assemblies of Mycoplasma bovis using a taxon-specific Bonito basecaller for MinION and Flongle long-read nanopore sequencing.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Nov 11;21(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03856-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 33176691 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

