Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension in the Southern Cone of Latin America
- PMID: 27543330
- PMCID: PMC5863773
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpw092
Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension in the Southern Cone of Latin America
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is the leading global preventable risk factor for premature death. While hypertension prevalence has been declining in high-income countries, it has increased continuously in low- and middle-income countries.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional survey in 7,524 women and men aged 35-74 years from randomly selected samples in 4 cities (Bariloche and Marcos Paz, Argentina; Temuco, Chile; and Pando-Barros Blancos, Uruguay) in 2010-2011. Three blood pressure (BP) measurements were obtained by trained observers using a standard mercury sphygmomanometer. Hypertension was defined as a mean systolic BP ≥140mm Hg and/or diastolic BP ≥90mm Hg and/or use of antihypertensive medications.
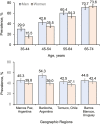
Results: An estimated 42.5% of the study population (46.6% of men and 38.7% of women) had hypertension and an estimated 32.5% (36.0% of men and 29.4% of women) had prehypertension. Approximately 63.0% of adults with hypertension (52.5% of men and 74.3% of women) were aware of their disease condition, 48.7% (36.1% of men and 62.1% of women) were taking prescribed medications to lower their BP, and only 21.1% of all hypertensive patients (13.8% of men and 28.9% of women) and 43.3% of treated hypertensive patients (38.1% of men and 46.5% of women) achieved BP control.
Conclusions: This study indicates that the prevalence of hypertension is high while awareness, treatment, and control are low in the general population in the Southern Cone of Latin America. These data call for bold actions at regional and national levels to implement effective, practical, and sustainable intervention programs aimed to improve hypertension prevention, detection, and control.
Keywords: Latin America; blood pressure; cross-sectional survey; hypertension; hypertension control; prevalence; risk factors..
© American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd 2016. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures

References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005; 365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A; International Society of Hypertension Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet 2008; 371:1513–1518. - PubMed
-
- Lim SS Vos T Flaxman AD Danaei G Shibuya K Adair-Rohani H Amann M Anderson HR Andrews KG Aryee M Atkinson C Bacchus LJ Bahalim AN Balakrishnan K Balmes J Barker-Collo S Baxter A Bell ML Blore JD Blyth F Bonner C Borges G Bourne R Boussinesq M, Brauer M Brooks P Bruce NG Brunekreef B Bryan-Hancock C Bucello C Buchbinder R Bull F Burnett RT Byers TE Calabria B Carapetis J Carnahan E Chafe Z Charlson F Chen H Chen JS Cheng AT Child JC Cohen A Colson KE Cowie BC Darby S Darling S Davis A Degenhardt L Dentener F Des Jarlais DC Devries K Dherani M Ding EL Dorsey ER Driscoll T Edmond K Ali SE Engell RE Erwin PJ Fahimi S Falder G Farzadfar F Ferrari A Finucane MM Flaxman S Fowkes FG Freedman G Freeman MK Gakidou E Ghosh S Giovannucci E Gmel G Graham K Grainger R Grant B Gunnell D Gutierrez HR Hall W Hoek HW Hogan A Hosgood HD 3rd Hoy D Hu H Hubbell BJ Hutchings SJ Ibeanusi SE Jacklyn GL Jasrasaria R Jonas JB Kan H Kanis JA Kassebaum N Kawakami N Khang YH Khatibzadeh S Khoo JP Kok C Laden F Lalloo R Lan Q Lathlean T Leasher JL Leigh J Li Y Lin JK Lipshultz SE London S Lozano R Lu Y Mak J Malekzadeh R Mallinger L Marcenes W March L Marks R Martin R McGale P McGrath J Mehta S Mensah GA Merriman TR Micha R Michaud C Mishra V Mohd Hanafiah K Mokdad AA Morawska L Mozaffarian D Murphy T Naghavi M Neal B Nelson PK Nolla JM Norman R Olives C Omer SB Orchard J Osborne R Ostro B Page A Pandey KD Parry CD Passmore E Patra J Pearce N Pelizzari PM Petzold M Phillips MR Pope D Pope CA 3rd Powles J Rao M Razavi H Rehfuess EA Rehm JT Ritz B Rivara FP Roberts T Robinson C Rodriguez-Portales JA Romieu I Room R Rosenfeld LC Roy A Rushton L Salomon JA Sampson U Sanchez-Riera L Sanman E, Sapkota A Seedat S Shi P Shield K Shivakoti R Singh GM Sleet DA Smith E Smith KR Stapelberg NJ Steenland K Stöckl H Stovner LJ Straif K Straney L Thurston GD Tran JH Van Dingenen R van Donkelaar A Veerman JL Vijayakumar L Weintraub R Weissman MM White RA Whiteford H Wiersma ST Wilkinson JD Williams HC Williams W Wilson N Woolf AD Yip P Zielinski JM Lopez AD Murray CJ Ezzati M AlMazroa MA Memish ZA. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012; 380:2224–2260. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988-2008. JAMA 2010; 303:2043–2050. - PubMed
-
- Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lin JK, Singh GM, Paciorek CJ, Cowan MJ, Farzadfar F, Stevens GA, Lim SS, Riley LM, Ezzati M; Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Blood Pressure) National, regional, and global trends in systolic blood pressure since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 786 country-years and 5·4 million participants. Lancet 2011; 377:568–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

