Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in 2016
- PMID: 27543499
- PMCID: PMC5862239
- DOI: 10.1093/bmb/ldw031
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in 2016
Abstract
Introduction: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the commonest cause of liver disease worldwide, and is rapidly becoming the leading indication for liver transplantation.
Sources of data: Original articles, reviews and meta-analyses, guidelines.
Areas of agreement: NAFLD strongly correlates with obesity and insulin resistance; currently, the best management strategy is weight loss and treatment of the metabolic syndrome.
Areas of controversy: Recent data suggest that the presence of fibrosis and not non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is the predictor of clinical outcome.
Growing points: Many phase 2 and 3 trials are underway. Drugs hoped to be effective are obeticholic acid, elafibranor, glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues and CCR2/5 inhibitors.
Areas timely for developing research: Improved understanding of the pathophysiology of NAFLD should help us identify which patients progress to significant liver disease and to develop therapies to target this population.
Keywords: NASH; assessment; cardiovascular disease; fibrosis; metabolic syndrome; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity; treatment.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
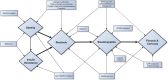
Figures

References
-
- Smits MM, Iannou GN, Boyko EJ, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as an independent manifestation of the metabolic syndrome: results of a US national survey in three ethnic groups. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;28:664–70. - PubMed
-
- Szczpaniak LS, Nurenburg P, Leonard D, et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content: prevalence of hepatic steatosis in the general population. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2005;288:462–8. - PubMed
-
- Visscher TLS, Heitmann BL, Rissanen A, et al. A break in the obesity epidemic? Explained by biases or misinterpretation of the data. Int J Obes 2005;39:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 2015;148:547–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

