Genome-wide recruitment profiling of transcription factor Crz1 in response to high pH stress
- PMID: 27544903
- PMCID: PMC4992276
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-3006-6
Genome-wide recruitment profiling of transcription factor Crz1 in response to high pH stress
Abstract
Background: Exposure of the budding Saccharomyces cerevisiae to an alkaline environment produces a robust transcriptional response involving hundreds of genes. Part of this response is triggered by an almost immediate burst of calcium that activates the Ser/Thr protein phosphatase calcineurin. Activated calcineurin dephosphorylates the transcription factor (TF) Crz1, which moves to the nucleus and binds to calcineurin/Crz1 responsive gene promoters. In this work we present a genome-wide study of the binding of Crz1 to gene promoters in response to high pH stress.
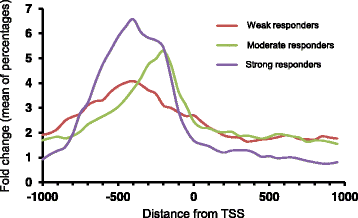
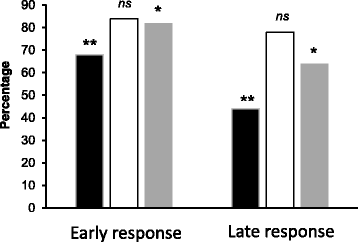
Results: Environmental alkalinization promoted a time-dependent recruitment of Crz1 to 152 intergenic regions, the vast majority between 1 and 5 min upon stress onset. Positional evaluation of the genomic coordinates combined with existing transcriptional studies allowed identifying 140 genes likely responsive to Crz1 regulation. Gene Ontology analysis confirmed the relevant impact of calcineurin/Crz1 on a set of genes involved in glucose utilization, and uncovered novel targets, such as genes responsible for trehalose metabolism. We also identified over a dozen of genes encoding TFs that are likely under the control of Crz1, suggesting a possible mechanism for amplification of the signal at the transcription level. Further analysis of the binding sites allowed refining the consensus sequence for Crz1 binding to gene promoters and the effect of chromatin accessibility in the timing of Crz1 recruitment to promoters.
Conclusions: The present work defines at the genomic-wide level the kinetics of binding of Crz1 to gene promoters in response to alkaline stress, confirms diverse previously known Crz1 targets and identifies many putative novel ones. Because of the relevance of calcineurin/Crz1 in signaling diverse stress conditions, our data will contribute to understand the transcriptional response in other circumstances that also involve calcium signaling, such as exposition to sexual pheromones or saline stress.
Keywords: Alkaline pH stress; Calcineurin signaling; Consensus binding sequence; Crz1 recruitment; Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Regulation of the Na+/K+-ATPase Ena1 Expression by Calcineurin/Crz1 under High pH Stress: A Quantitative Study.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 30;11(6):e0158424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158424. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27362362 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol stress stimulates the Ca2+-mediated calcineurin/Crz1 pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biosci Bioeng. 2009 Jan;107(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2008.09.005. J Biosci Bioeng. 2009. PMID: 19147100
-
The transcriptional response to alkaline pH in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for calcium-mediated signalling.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Dec;46(5):1319-33. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03246.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12453218
-
Calcineurin-Crz1 signaling in lower eukaryotes.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Jun;13(6):694-705. doi: 10.1128/EC.00038-14. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 24681686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CRaZy Calcium Cycle.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;892:169-186. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25304-6_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26721274 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic profiling of the yeast Komagataella phaffii in response to environmental alkalinization.Microb Cell Fact. 2023 Apr 4;22(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02074-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2023. PMID: 37013612 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing alkaline-pH regulatable promoters for efficient methanol-free expression of enzymes of industrial interest in Komagataella Phaffii.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Apr 2;23(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02362-9. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 38566096 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the reserve carbohydrate metabolism by alkaline pH and calcium in Neurospora crassa reveals a possible cross-regulation of both signaling pathways.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jun 9;18(1):457. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3832-1. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28599643 Free PMC article.
-
A glycosylated Phr1 protein is induced by calcium stress and its expression is positively controlled by the calcium/calcineurin signaling transcription factor Crz1 in Candida albicans.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 18;21(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01224-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37723578 Free PMC article.
-
CRZ1 regulator and calcium cooperatively modulate holocellulases gene expression in Trichoderma reesei QM6a.Genet Mol Biol. 2020 May 8;43(2):e20190244. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0244. eCollection 2020. Genet Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32384133 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

