IL-21/IL-21R signaling suppresses intestinal inflammation induced by DSS through regulation of Th responses in lamina propria in mice
- PMID: 27545302
- PMCID: PMC4992961
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31881
IL-21/IL-21R signaling suppresses intestinal inflammation induced by DSS through regulation of Th responses in lamina propria in mice
Abstract
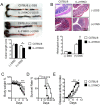
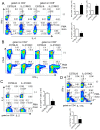
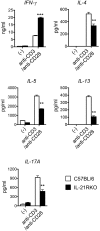
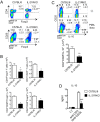
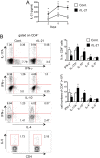
Serum level of IL-21 is increased in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), suggesting that IL-21/IL-21 receptor (IL-21R) signaling may be involved in the pathogenesis of IBD. However, the role of IL-21/IL-21 receptor signaling plays in the pathogenesis of IBD is not very clear. In this study, using IL-21R.KO mice, we tested the role of IL-21/IL-21R signaling in the regulation of T helper cell responses during intestinal inflammation. Here we found that IL-21R.KO mice were more susceptible to DSS-induced colitis as compared with C57BL/6 mice. The spontaneous inflammatory cytokines released by macrophages in LP of colon were significantly increased, and Th2, Th17 and Treg responses were down-regulated markedly. However, Th1 responses were significantly up-regulated in IL-21R.KO mice. Meanwhile, the population of CD8(+)CD44(+)IFN-γ(+) T cells was markedly elevated in LP of inflammatory intestine of IL-21RKO mice. In vivo, after disease onset, DSS-induced intestinal inflammation was ameliorated in C57BL/6 mice treated with rIL-21. Our results demonstrate that IL-21/IL-21R signaling contributes to protection against DSS-induced acute colitis through suppression of Th1 and activation of Th2, Th17 and Treg responses in mice. Therefore, therapeutic manipulation of IL-21/IL-21R activity may allow improved immunotherapy for IBD and other inflammatory diseases associated with Th cell responses.
Figures



Similar articles
-
IL-33 induces both regulatory B cells and regulatory T cells in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 May;46:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.02.006. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28258042
-
Regulation of gut inflammation and th17 cell response by interleukin-21.Gastroenterology. 2008 Apr;134(4):1038-48. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.041. Epub 2008 Jan 17. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18395085
-
Interleukin-36β exacerbates DSS-induce acute colitis via inhibiting Foxp3+ regulatory T cell response and increasing Th2 cell response.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Jul;108:108762. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108762. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35436743
-
Immunoregulatory Pathways Involved in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015 Sep;21(9):2188-93. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000477. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015. PMID: 26111210 Review.
-
Interleukin (IL)-21 in Inflammation and Immunity During Parasitic Diseases.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Dec 4;9:401. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00401. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31867283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin 21 collaborates with interferon-γ for the optimal expression of interferon-stimulated genes and enhances protection against enteric microbial infection.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Feb 28;15(2):e1007614. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007614. eCollection 2019 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30818341 Free PMC article.
-
Brusatol-Enriched Brucea javanica Oil Ameliorated Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice: Involvement of NF-κB and RhoA/ROCK Signaling Pathways.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Aug 9;2021:5561221. doi: 10.1155/2021/5561221. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34414236 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21 mediates microRNA-423-5p /claudin-5 signal pathway and intestinal barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Aug 28;12(16):16099-16110. doi: 10.18632/aging.103566. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32855360 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Associated Colorectal Cancer: Translational Risks from Mechanisms to Medicines.J Crohns Colitis. 2021 Dec 18;15(12):2131-2141. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab102. J Crohns Colitis. 2021. PMID: 34111282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of IL-10 signaling in macrophages limits bacterial killing driven by prostaglandin E2.J Exp Med. 2020 Feb 3;217(2):e20180649. doi: 10.1084/jem.20180649. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 31819956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scaldaferri F. & Fiocchi C. Inflammatory bowel disease progress and current concepts of etiopathogenesis. J Dig Dis. 8, 171–178 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Xavier R. J. & Podolsky D. K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 448, 427–434 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Mizoguchi A., Mizoguchi E. & Bhan A. K. The critical role of interleukin 4 but not interferon gamma in the pathogenesis of colitis in T-cell receptor alpha mutant mice. Gastroenterology 116, 320–326 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

