Analgesic Efficacy of a New Immediate-Release/Extended-Release Formulation of Ibuprofen: Results From Single- and Multiple-Dose Postsurgical Dental Pain Studies
- PMID: 27545511
- PMCID: PMC6093260
- DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.297
Analgesic Efficacy of a New Immediate-Release/Extended-Release Formulation of Ibuprofen: Results From Single- and Multiple-Dose Postsurgical Dental Pain Studies
Abstract
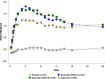
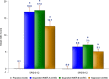
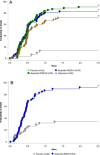
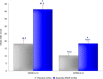
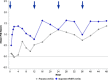
Analgesic effects of ibuprofen immediate-release/extended-release (IR/ER) 600-mg tablets were evaluated in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled dental pain studies. Patients 16-40 years old with moderate-severe pain following third-molar extraction received single-dose ibuprofen 600 mg IR/ER (formulation A or B), naproxen sodium 220 mg, or placebo (2:2:2:1; study 1) or 4 doses of ibuprofen 600 mg IR/ER (formulation A) or placebo (1:1; study 2). In study 1 (n = 196), mean (standard deviation [SD]) time-weighted sum of pain intensity difference scores for placebo, ibuprofen IR/ER A, ibuprofen IR/ER B, and naproxen, respectively, were 0.05 (9.2), 16.87 (9.4), 17.34 (10.5), and 12.66 (10.0) over 0-12 hours and -0.03 (4.1), 6.57 (4.4), 7.14 (5.2), and 5.14 (5.0) over 8-12 hours (all P < .001 vs placebo). In study 2 (n = 106), mean (SD) time-weighted sum of pain relief and pain intensity difference scores were 18.2 (20.0) versus 41.5 (21.0) at 0-12 hours and 10.3 (12.0) versus 18.4 (12.1) at 8-12 hours for placebo versus ibuprofen IR/ER, respectively (P < .001 for both); efficacy was sustained over each of the four 12-hour dosing intervals with ibuprofen. Gastrointestinal adverse events predominated with placebo both after study medication administration and after rescue medication use, if applicable. Ibuprofen 600 mg IR/ER provided safe and effective analgesia after single and multiple doses.
Keywords: analgesia; dental pain; extended release; ibuprofen; immediate release.
© 2016, The American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A single-tablet fixed-dose combination of racemic ibuprofen/paracetamol in the management of moderate to severe postoperative dental pain in adult and adolescent patients: a multicenter, two-stage, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, factorial study.Clin Ther. 2010 Jun;32(6):1033-49. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.06.002. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20637958 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of single-dose, extended-release naproxen sodium 660 mg in postsurgical dental pain: two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials.Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(2):331-42. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1123680. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016. PMID: 26588111 Clinical Trial.
-
Longer analgesic effect with naproxen sodium than ibuprofen in post-surgical dental pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-dose trial.Curr Med Res Opin. 2019 Dec;35(12):2149-2158. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2019.1655257. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019. PMID: 31402718 Clinical Trial.
-
Diclofenac potassium 12.5mg tablets for mild to moderate pain and fever: a review of its pharmacology, clinical efficacy and safety.Clin Drug Investig. 2007;27(3):163-95. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200727030-00002. Clin Drug Investig. 2007. PMID: 17305413 Review.
-
The use of COX-2 inhibitors for acute dental pain: A second look.J Am Dent Assoc. 2006 Apr;137(4):480-7. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2006.0220. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006. PMID: 16637477 Review.
Cited by
-
A Meta-Analysis of the Analgesic Efficacy of Single-Doses of Ibuprofen Compared to Traditional Non-Opioid Analgesics Following Third Molar Surgery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Apr 14;14(4):360. doi: 10.3390/ph14040360. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Combination of NSAIDs and Muscle Relaxants in the Management of Acute Low Back Pain.Pain Ther. 2019 Jun;8(1):121-132. doi: 10.1007/s40122-019-0112-6. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Pain Ther. 2019. PMID: 30652262 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework with scu-c Topology for Drug Delivery.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Oct 26;14(42):48045-48051. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c15152. Epub 2022 Oct 17. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 36252155 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of E-PR-01 on Activity-Induced Acute Knee Joint Discomfort in Healthy Individuals: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Cross-Over Study.J Pain Res. 2023 Jun 23;16:2141-2153. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S412018. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 37384126 Free PMC article.
-
Ibuprofen for acute postoperative pain in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 5;1(1):CD015432. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015432.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38180091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rainsford KD. Fifty years of ibuprofen: advancing pain and fever management. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2013(178):1–2. - PubMed
-
- Rainsford KD. Ibuprofen: from invention to an OTC therapeutic mainstay. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2013(178):9–20. - PubMed
-
- Cooper SA, Schachtel BP, Goldman E, Gelb S, Cohn P. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen in the relief of acute pain: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;29(11):1026–1030. - PubMed
-
- Schachtel BP, Fillingim JM, Thoden WR, Lane AC, Baybutt RI. Sore throat pain in the evaluation of mild analgesics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988;44(6):704–711. - PubMed
-
- Schachtel BP, Thoden WR, Baybutt RI. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen in the relief of postpartum episiotomy pain. J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;29(6):550–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

