High molecular weight PEGylation of human pancreatic polypeptide at position 22 improves stability and reduces food intake in mice
- PMID: 27545829
- PMCID: PMC5071565
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13582
High molecular weight PEGylation of human pancreatic polypeptide at position 22 improves stability and reduces food intake in mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Human pancreatic polypeptide (hPP) is known to suppress appetite and food intake, thereby representing a potential therapeutic approach against obesity and associated metabolic disorders. The aim of this study was to improve hPP stability by covalent PEGylation with diverse molecular weight polyethylene glycols (PEGs) at two positions using promising lead structures while maintaining target activity.
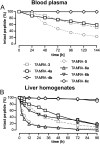
Experimental approach: Modified peptides were synthesized by combined solid-phase and solution-phase peptide synthesis. Their potency was investigated in constitutively expressing human epithelial cells and isolated human colonic mucosa as well as receptor-transfected artificial cell lines. Human blood plasma and porcine liver homogenates were used to examine the in vitro stability of the analogues. The most promising variants were injected s.c. in C57BL/6JRj mice to monitor fasting-induced food intake and bioavailability.
Key results: In human epithelia and colonic mucosal preparations, activity of the modified hPP peptides depended on the core sequence and latency of the peptides was related to PEG size. Peptides modified with a 22 kDa PEG (PEG22) remained intact in blood plasma and on incubation with liver homogenates for more than 96 h. Finally, hPP2-36 , [K22 (PEG22)]hPP2-36 and [K22 (PEG22),Q34 ]hPP significantly reduced cumulative food intake in mice over 16 h after s.c. administration.
Conclusions and implications: Modification with PEG22 at position 22 stabilizes hPP significantly while extending its biological activities and could be used in drug development prospectively.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-acting lipidated analogue of human pancreatic polypeptide is slowly released into circulation.J Med Chem. 2011 Apr 28;54(8):2658-67. doi: 10.1021/jm101357e. Epub 2011 Mar 31. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21410292
-
Position and length of fatty acids strongly affect receptor selectivity pattern of human pancreatic polypeptide analogues.ChemMedChem. 2014 Nov;9(11):2463-74. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201402235. Epub 2014 Aug 22. ChemMedChem. 2014. PMID: 25156249 Free PMC article.
-
PEGylation of (99m)Tc-labeled bombesin analogues improves their pharmacokinetic properties.Nucl Med Biol. 2011 Oct;38(7):997-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2011.02.014. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Nucl Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21982571
-
The impact of PEGylation on biological therapies.BioDrugs. 2008;22(5):315-29. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200822050-00004. BioDrugs. 2008. PMID: 18778113 Review.
-
Gut hormones as peripheral anti obesity targets.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004 Oct;3(5):379-88. doi: 10.2174/1568007043336950. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. PMID: 15544446 Review.
Cited by
-
Receptor-specific recognition of NPY peptides revealed by structures of NPY receptors.Sci Adv. 2022 May 6;8(18):eabm1232. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm1232. Epub 2022 May 4. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35507650 Free PMC article.
-
Novel enzyme-resistant pancreatic polypeptide analogs evoke pancreatic beta-cell rest, enhance islet cell turnover, and inhibit food intake in mice.Biofactors. 2024 Nov-Dec;50(6):1101-1112. doi: 10.1002/biof.2059. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Biofactors. 2024. PMID: 38635341 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Assembled Peptide Hydrogels PPI45 and PPI47: Novel Drug Candidates for Staphylococcus aureus Infection Treatment.Gels. 2025 Jan 13;11(1):63. doi: 10.3390/gels11010063. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39852034 Free PMC article.
-
Intrauterine growth restriction alters growth performance, plasma hormones, and small intestinal microbial communities in growing-finishing pigs.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2020 Aug 19;11:86. doi: 10.1186/s40104-020-00490-x. eCollection 2020. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32832077 Free PMC article.
-
Designing Formulation Strategies for Enhanced Stability of Therapeutic Peptides in Aqueous Solutions: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 14;15(3):935. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030935. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asakawa A, Inui A, Ueno N, Fujimiya M, Fujino MA, Kasuga M (1999). Mouse pancreatic polypeptide modulates food intake, while not influencing anxiety in mice. Peptides 20: 1445–1448. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

