Surface thermal oxidation on titanium implants to enhance osteogenic activity and in vivo osseointegration
- PMID: 27546196
- PMCID: PMC4992888
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31769
Surface thermal oxidation on titanium implants to enhance osteogenic activity and in vivo osseointegration
Abstract
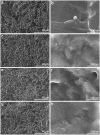
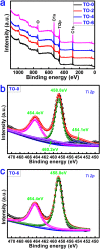
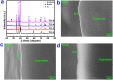
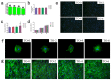
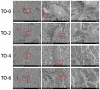
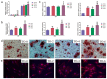
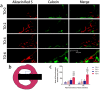
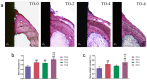
Thermal oxidation, which serves as a low-cost, effective and relatively simple/facile method, was used to modify a micro-structured titanium surface in ambient atmosphere at 450 °C for different time periods to improve in vitro and in vivo bioactivity. The surface morphology, crystallinity of the surface layers, chemical composition and chemical states were evaluated by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Cell behaviours including cell adhesion, attachment, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation were observed in vitro study. The ability of the titanium surface to promote osseointegration was evaluated in an in vivo animal model. Surface thermal oxidation on titanium implants maintained the microstructure and, thus, both slightly changed the nanoscale structure of titanium and enhanced the crystallinity of the titanium surface layer. Cells cultured on the three oxidized titanium surfaces grew well and exhibited better osteogenic activity than did the control samples. The in vivo bone-implant contact also showed enhanced osseointegration after several hours of oxidization. This heat-treated titanium enhanced the osteogenic differentiation activity of rBMMSCs and improved osseointegration in vivo, suggesting that surface thermal oxidation could potentially be used in clinical applications to improve bone-implant integration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multifunctions of dual Zn/Mg ion co-implanted titanium on osteogenesis, angiogenesis and bacteria inhibition for dental implants.Acta Biomater. 2017 Feb;49:590-603. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.067. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27915020
-
Electrochemical Deposition of Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite Coating on Titanium with Enhanced Early Stage Osteogenic Activity and Osseointegration.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Sep 8;15:6605-6618. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S268372. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32982221 Free PMC article.
-
Modified surface morphology of a novel Ti-24Nb-4Zr-7.9Sn titanium alloy via anodic oxidation for enhanced interfacial biocompatibility and osseointegration.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 Aug 1;144:265-275. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.04.020. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 27100853
-
Nano-scale modification of titanium implant surfaces to enhance osseointegration.Acta Biomater. 2019 Aug;94:112-131. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.045. Epub 2019 May 22. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31128320 Review.
-
Effects of titanium nanotubes on the osseointegration, cell differentiation, mineralisation and antibacterial properties of orthopaedic implant surfaces.Bone Joint J. 2018 Jan;100-B(1 Supple A):9-16. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B1.BJJ-2017-0551.R1. Bone Joint J. 2018. PMID: 29292334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Nano-hydroxyapatite-coated Implants against Peri-implantitis Bacteria.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025 Jun;17(Suppl 2):S1595-S1597. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_162_25. Epub 2025 Jun 18. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025. PMID: 40655852 Free PMC article.
-
Amorphous TiO2nano-coating on stainless steel to improve its biological response.Biomed Mater. 2024 Aug 21;19(5):055037. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ad6dc4. Biomed Mater. 2024. PMID: 39121890 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the electrochemical characteristics of titanium on the adsorption kinetics of albumin.RSC Adv. 2019 Oct 24;9(59):34265-34273. doi: 10.1039/c9ra05988a. eCollection 2019 Oct 23. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35529982 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Substrate Type in the Process of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Formation.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 24;14(13):2566. doi: 10.3390/polym14132566. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808612 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Electrical Parameters on Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings on Pure Titanium.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;14(10):1950. doi: 10.3390/mi14101950. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37893387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geetha M., Singh A. K., Asokamani R. & Gogia A. K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants – A review. Progress in Materials Science 54, 397–425 (2009).
-
- Liu X., Chu P. K. & Ding C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports 47, 49–121 (2004).
-
- Kulangara K. & Leong K. W. Substrate topography shapes cell function. Soft Matter 5, 4072–4076 (2009).
-
- Williams D. F. On the nature of biomaterials. Biomaterials 30, 5897–5909 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Higuchi A., Ling Q.-D., Chang Y., Hsu S.-T. & Umezawa A. Physical Cues of Biomaterials Guide Stem Cell Differentiation Fate. Chemical Reviews 113, 3297–3328 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

