Linagliptin monotherapy compared with voglibose monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing hemodialysis: a 12-week randomized trial
- PMID: 27547421
- PMCID: PMC4964246
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2016-000265
Linagliptin monotherapy compared with voglibose monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing hemodialysis: a 12-week randomized trial
Abstract
Objective: Focusing on efficacy and tolerability, we compared linagliptin monotherapy with voglibose monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing hemodialysis (HD).
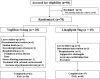
Research design and methods: In this multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel-group, active-controlled study, 78 patients were randomized (1:1) to receive a 12-week treatment with 5 mg linagliptin once daily or 0.2 mg voglibose three times a day. To assess whether linagliptin was superior to voglibose, the primary efficacy end point was the change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level between baseline and week 12. Secondary efficacy end points included changes between baseline and week 12 in glycated albumin (GA) and casual plasma glucose (PG) levels.
Results: At week 12, the adjusted mean HbA1c levels had decreased by -0.60% after treatment with linagliptin and by -0.20% after treatment with voglibose (treatment difference: -0.40%, 95% CI -0.74% to -0.06%, p=0.022). A significant reduction in casual PG level was also observed after treatment with linagliptin compared with treatment with voglibose. Relative to voglibose, linagliptin tended to elicit reductions in GA, although without statistical significance. No hypoglycemic symptoms or severe hypoglycemia occurred during the study.
Conclusions: In patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing HD, linagliptin monotherapy provided significantly better glycemic control without severe hypoglycemia than voglibose monotherapy. Linagliptin represents a promising agent for glycemic management in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing HD.
Trial registration number: UMIN000007635; results.
Keywords: A1C; Nephropathy; Oral Antidiabetics.
Figures
References
-
- Shurraw S, Hemmelgarn B, Lin M et al. , Alberta Kidney Disease Network. Association between glycemic control and adverse outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: a population-based cohort study. Arch Intern Med 2011;171:1920–7. - PubMed
-
- Morioka T, Emoto M, Tabata T et al. . Glycemic control is a predictor of survival for diabetic patients on hemodialysis. Diabetes Care 2001;24:909–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources